
This post contains the whole syllabus of 3rd BHMS (theory and practical). This is prepared for the purpose of providing the whole idea of learning objectives in each subject.
This syllabus is applicable from the academic session 2015-2016, as per the guidelines of Central Council of Homoeopathy (India).
Subjects to be taught in 3rd BHMS
- SURGERY
- GYNAECOLOGY AND OBSTETRICS
- HOMOEOPATHIC MATERIA MEDICA
- ORGANON OF MEDICINE
- PRACTICE OF MEDICINE
- COMMUNITY MEDIINE
- REPERTORY
Before going through the detail, you should know that out of mainly 7 subjects you will have to give exam of only 4 subjects.
- GYNAECOLOGY AND OBSTETRICS
- SURGERY
- HOMOEOPATHIC MATERIA MEDICA
- ORGANON OF MEDICINE
If you want to prepare for the University examination you should follow the below mentioned links,
Table of Contents
Toggle3rd BHMS SURGERY SYLLABUS
Students who are going to learn Surgery should keep in mind that,
- Knowledge of Anatomy is important for proper understanding of surgery subject.
- Learn the fundamentals of physical examination of the patients with surgical problems.
- You should be able to diagnose common surgical conditions by the end of the year.
- Learn to organize pre- and post-operative homoeopathic medical care.
Theory syllabus
Systemic Surgery
- Diseases of blood vessels, lymphatics and peripheral nerves
- Diseases of glands
- Diseases of extremities
- Diseases of thorax and abdomen
- Diseases of alimentary tract
- Diseases of liver, spleen, gall bladder and bile duct,
- Diseases of abdominal wall, umbilicus, hernias.
- Diseases of heart and pericardium.
- Diseases of urogenital system.
- Diseases of the bones, cranium, vertebral column, fractures and dislocations.
- Diseases of the joints.
- Diseases of the muscles, tendons and fascia.
Ear
- Applied anatomy and applied physiology of ear
- Examination of ear
- Diseases of external, middle and inner ear
Nose
- Applied anatomy and physiology of nose and paranasal sinuses.
- Examination of nose and paranasal sinuses
- Diseases of nose and paranasal sinuses
Throat
- Applied anatomy and applied physiology of pharynx, larynx, tracheobronchial tree, oesophagus
- Examination of pharynx, larynx, tracheobronchial tree, oesophagus
- Diseases of throat (external and internal)
- Diseases of oesophagus.
Ophthalmology
- Applied anatomy, physiology of eye
- Examination of eye.
- Diseases of eyelids, eyelashes and lacrimal drainage system.
- Diseases of eyes including injury related problems.
Dentistry
- Applied anatomy, physiology of teeth and gums;
- Milestones related to teething.
- Examination of oral cavity.
- Diseases of gums
- Diseases of teeth
- Problems of dentition
General management, surgical management and Homoeopathic therapeutics of the above topics will be covered.
Practical or clinical syllabus:
(To be taught in Second and Third B.H.M.S.)
- Every student shall prepare and submit twenty complete histories of surgical cases, ten each in the Second and Third B.H.M.S. classes respectively.
- Demonstration of surgical instruments, X-rays, specimens etc.
- Clinical examinations in surgery.
- Management of common surgical procedures and emergency procedures as stated below:
- Wounds
- Abscesses: incision and drainage.
- Dressings and plasters.
- Suturing of various types.
- Pre-operative and post-operative care.
- Management of shock.
- Management of acute haemorrhage.
- Management of acute injury cases.
- Preliminary management of a head Injury
3rd BHMS GYNECOLOGY AND OBSTETRICS SYLLABUS
Students should keep in mind while studying Gynaecology and Obstetrics,
- Proper knowledge of anatomy and physiology of female reproductive system is compulsory.
- Revise the endocrine system for proper understanding of female hormones.
- Learn the clinical methods of investigation properly.
- Special attention should be given in case of pregnant women.
- Learn the methods of proper care of new born.
- Homoeopathy has vast scope in gynaecological and obstetrical conditions that should be learnt properly.
Theory syllabus
Gynaecology
- Infections and ulcerations of the female genital organs.
- Injuries of the genital tract.
- Disorders of menstruation.
- Menorrhagia and dysfunctional uterine bleeding.
- Disorders of female genital tract.
- Diseases of breasts.
- Sexually transmitted diseases.
- Endometriosis and adenomyosis.
- Infertility and sterility,
- Non-malignant growths,
- Chemotherapy caused complications.
- Management and therapeutics of the above listed topics in Gynaecology.
Obstetrics
- High risk labour; mal-positions and mal-presentations; twins, prolapse of cord and limbs, abnormalities in the action of the uterus; abnormal conditions of soft part contracted pelvis; obstructed labour, complications of 3rd stage of labour, injuries of birth canal, foetal anomalies.
- Abnormal pregnancies-abortions, molar pregnancy, diseases of placenta and membranes, toxaemia of pregnancy, antepartum haemorrhages, multiple pregnancy, protracted gestation, ectopic pregnancy, intrauterine growth retardation, pregnancy in Rh negative woman, intrauterine foetal death, still birth.
- Common disorders and systemic diseases associated with pregnancy.
- Pre-natal Diagnostic Techniques-PNDT (regulation and prevention of misuse) Act, 1994.
- Common obstetrical operations-medical termination of pregnancy, criminal abortion, caesarean section, episiotomy.
- Emergency obstetric care.
- Population dynamics and control of conception.
- Infant care – neonatal hygiene, breast feeding, artificial feeding, management of premature child, asphyxia, birth injuries, common disorders of newborn.
- Reproductive and child health care (a) safe motherhood and child survival (b) Risk approach- MCH care (c) Maternal mortality and morbidity (d) Prenatal mortality and morbidity (e) Diseases of foetus and new born.
- Medico-legal aspects in obstetrics.
Homoeopathic management and therapeutics of the above listed clinical conditions in obstetrics.
Practical or clinical syllabus
Practical or clinical classes shall be taken on the following topics both in Second and Third B.H.M.S.
- Gynaecological case taking
- Obstetrical case taking
- Gynaecological examination of the patient obstetrical examination of the patient including antenatal, intranatal and post- natal care.
- Bed side training
- Adequate grasp over Homoeopathic principles and management.
- Identification of Instruments and models Record of ten cases each in gynaecology and obstetrics.
3rd BHMS MATERIA MEDICA SYLLABUS
Students who are going to learn Materia medica in 3rd BHMS should keep in mind that,
- With the progression of years number of medicines will also get increased so frequent revisions will help you for long time.
- Do not get confused from so many references, you will end up mixing the medicines.
- Preparing notes of Materia medica will come handy especially when you will have to learn from multiple Materia medica with so many drugs.
Knowledge of materia medica will also help you in homoeopathic therapeutics.
When I was a student, I prepared a materia medica note for all the medicines of syllabus with the reference of 2 to 4 good materia medica. I found it helpful because,
- My concepts were so clear after this exercise.
- I was able to find all the rare symptoms from different books at one place.
- I did not have to carry multiple books at the time of viva examination for revision.
- I did not have to waste my time for searching of medicine from this book to that one.
- I was fully prepared with all medicines (without missing single one) of syllabus as I had written all of them in my notes, I just had to read and revise them one by one.
In addition to the syllabus of First B.H.M.S. and Second B.H.M.S. including the use of medicines for 2nd BHMS, the following additional topics and medicines are included in the syllabus of Homoeopathic material medica for the Third B.H.M.S examination.
General topics of homoeopathic materia medica
- Concept of nosodes – Definition of nosodes, types of nosodes, general indications of nosodes.
- Concepts of constitution, temperaments, diathesis definitions, various concepts of constitution with their peculiar characteristics, importance of constitution temperaments and diathesis and their utility in treatment of patients.
- Concept of mother tincture.
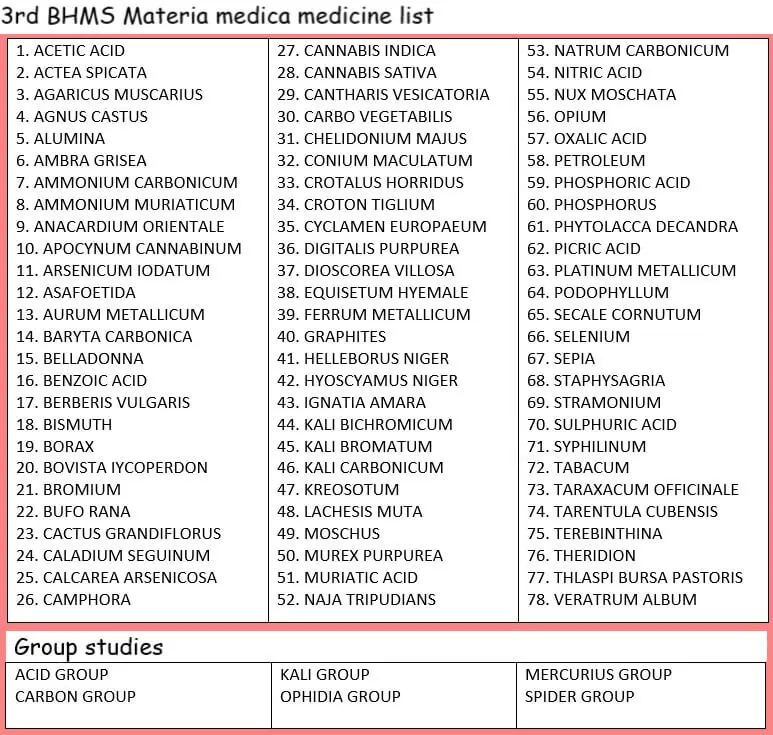
Homoeopathic medicines to be taught in 3rd B.H.M.S. are
3rd BHMS ORGANON OF MEDICINE SYLLABUS
Students of 3rd BHMS who are studying organon of medicine should keep in mind that,
- Even though the number of topics will be increasing with upcoming years, you will find its easy to remember the topics of Organon of medicine and philosophy.
- Just make sure that your concepts are very clear.
Theory syllabus
In addition to revision of Aphorisms studied in First B.H.M.S and Second B.H.M.S, the following topics shall be covered, namely;
- Hahnemann ‘s Prefaces and Introduction to Organon of Medicine.
- Aphorisms 105 to 294 of Hahnemann ‘s Organon of Medicine, including foot notes (5th and 6th Editions translated by R.E. Dudgeon and W. Boericke)
- Chapters of philosophy books of J.T. Kent (Chapters- 28, 29, 30, 34 to 37), Stuart Close (Chapters- 7, 10, 13, 14, 15) & H.A. Roberts (Chapters- 7, 10, 12 to 19,21, 34) related to 105-294 Aphorisms of Organon of Medicine.
Practical or clinical syllabus
Each student appearing for 3rd B.H.M.S examination shall maintain records of 20 cases (10 acute and 10 chronic cases).
3rd BHMS PRACTICE OF MEDIICNE SYLLABUS
Applied anatomy and applied physiology of the respective system as stated below.
- Respiratory diseases.
- Diseases of digestive system and peritoneum.
- Diseases concerning liver, gall-bladder and pancreas.
- Genetic Factors (co-relating diseases with the concept of chronic Miasms).
- Immunological factors in diseases with concept of susceptibility (including HIV, Hepatitis-B).
- Disorders due to chemical and physical agents and to climatic and environmental factors.
- Knowledge of clinical examination of respective systems.
- Water and electrolyte balance – disorders of.
3rd BHMS COMMUNITY MEDICINE SYLLABUS
There will be no examination of community medicine subject in 3rd B.H.M.S
- Man and medicine
- Concept of health and disease in conventional medicine and homoeopathy
- Nutrition and health
- Food and nutrition
- Food in relation to health and disease
- Balanced diet — Nutritional deficiencies, and nutritional survey
- Food processing
- Pasteurization of milk
- Adulteration of food
- Food poisoning
- Environment and health
- Air, light and sunshine, radiation
- Effect of climate
- Comfort zone
- Personal hygiene
- Physical exercise
- Sanitation of fair and festivals
- Disinfection and sterilization
- Atmospheric pollution and purification of air
- Air borne diseases
- Water
- Distribution of water; uses; impurities and purification
- Standards of drinking water
- Water borne diseases
- Excreta disposal
- Disposal of deceased
- Disposal of refuse
- Medical entomology- insecticides, disinfection, Insects in relation to disease, Insect control
- Occupational health
- Preventive medicine in paediatrics and geriatrics
3rd BHMS REPERTORY SYLLABUS
There will be no Examination of Repertory subject in 3rd B.H.M.S.
Theory syllabus
Repertory: Definition; Need; Scope and Limitations.
Classification of repertories
Study of different repertories (Kent, Boenninghausen, Boger-Boenninghausen):
- History
- Philosophical background
- Structure
- Concept of repertorisation
- Adaptability
- Scope
- Limitations
Gradation of remedies by different authors.
Methods and techniques of repertorisation. Steps of repertorisation.
Terms and language of repertories (rubrics) cross references in other repertories and materia medica.
Conversion of symptoms into rubrics and repertorisation using different repertories.
Repertory – its relation with organon of medicine and materia medica.
Case taking and related topics:
- Case taking.
- Difficulties of case taking, particularly in a chronic case.
- Types of symptoms, their understanding and importance.
- Importance of pathology in disease diagnosis and individualization in relation to study of repertory.
Case processing
- Analysis and evaluation of symptoms
- Miasmatic assessment
- Totality of symptoms or conceptual image of the patient
- Repertorial totality
- Selection of rubrics
- Reportorial technique and results
- Repertorial analysis
Practical or clinical syllabus
- Record of five cases each of surgery, gynaecology and obstetrics worked out by using Kent’s repertory.
- Rubrics hunting from Kent’s & Boenninghausen’s repertories.













Leave a Reply