This post is about Endocrinology of Adrenal Cortex/Adrenocorticoids.
You will learn how important they are to sustain normal healthy human life.
This post will cover all three groups of adrenal cortex hormones with their important functions.
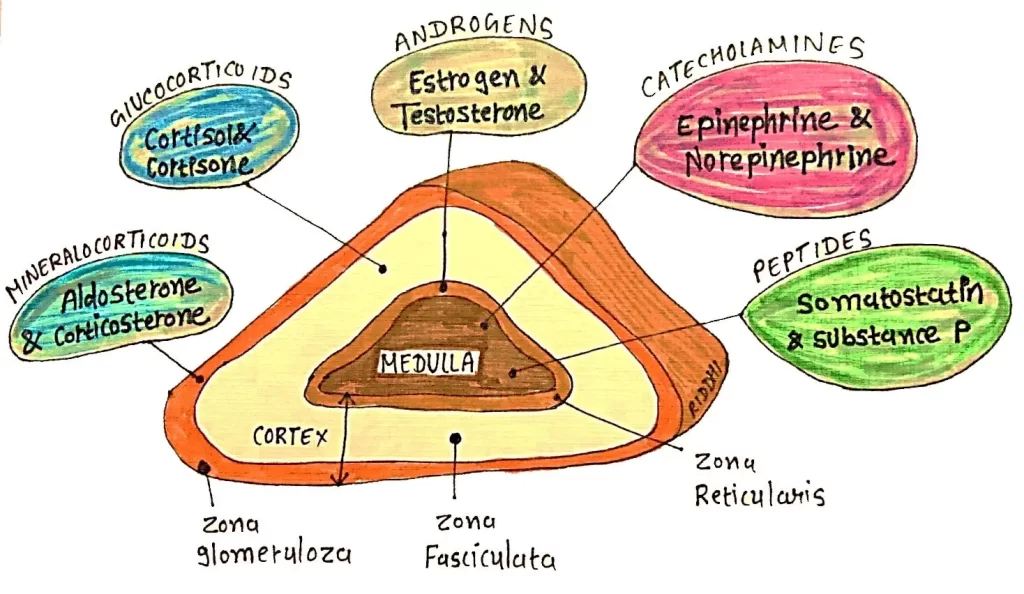
ADRENAL CORTEX
- Adrenal glands are called the ‘Life-saving glands’ or ‘Essential endocrine glands’.
- It is because, the absence of adrenocortical hormones causes death within 3 to 15 days and absence of adrenomedullary hormones,
drastically decreases the resistance to mental and physical stress. - Adrenocortical hormones are steroids in nature, hence the name ‘Corticosteroids’
- Based on their functions, classified into three groups:
- Mineralocorticoids
- Glucocorticoids
- Sex hormones.
Out of these, Glucocorticoids and Mineralocorticoids are the major hormones secreted by Adrenal Cortex.
Table of Contents
ToggleMINERALOCORTICOIDS
Mineralocorticoids are corticosteroids that act on minerals [electrolytes].
Mineralocorticoids are:
- Aldosterone
- 11-deoxycorticosterone
SOURCE OF SECRETION
From Zona glomerulosa of adrenal cortex.
FUNCTIONS OF MINERALOCORTICOIDS (ACTIONS OF ALDOSTERONE)
1) Majority of mineralocorticoid activity is provided by Aldosterone.
2) Aldosterone acts on distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct and increases the reabsorption of sodium.
- When sodium ions are reabsorbed from renal tubules, simultaneously water is also reabsorbed.
- Water reabsorption is almost equal to sodium reabsorption, so there is increase in ECF volume and blood volume.
- Increase in ECF volume and blood volume finally leads to increase in blood pressure.
3) Increases potassium excretion through renal tubules.
4) Causes tubular secretion of hydrogen ions & reduces hydrogen ion concentration in ECF.
5) Helps in conservation of sodium in body by absorbing it from saliva and sweat.
6) Increases sodium absorption from intestine.
MODE OF ACTION
- Since aldosterone is lipid soluble, it diffuses readily into cytoplasm of tubular epithelial cells.
- Where it binds with specific receptor protein and makes Aldosterone-receptor complex.
↓
- Which diffuses into nucleus where it binds to DNA and causes formation of mRNA.
↓
- mRNA causes protein synthesis (sodium potassium ATPase).
↓
- Which helps in transport of sodium and potassium.
REGULATION OF SECRETION
Aldosterone secretion is regulated by Four important factors,
1. Increase in potassium ion (K+) concentration in ECF.
2. Decrease in sodium ion (Na+) concentration in ECF.
3. Decrease in ECF volume.
4. Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH).
1) Increase in concentration of K+ is most effective stimulant It acts directly on zona glomerulosa and increases secretion of Aldosterone.
2) Decrease in Na+ concentration & ECF volume stimulates Aldosterone secretion through Renin-Angiotensin mechanism.
- Renin secreted from juxtaglomerular apparatus of kidney acts on Angiotensinogen in plasma and converts it into Angiotensin I.
- Angiotensin I is converted into Angiotensin II by converting enzyme (ACE) secreted by lungs.
- Angiotensin II acts on zona glomerulosa to secrete more
aldosterone. - Aldosterone in turn, increases retention of Na+ and water and excretion of k+.
- This leads to increase in Na+ concentration and ECF volume (So, Renin’s primary function is to increase in the blood pressure).
Now, it inhibits juxtaglomerular apparatus and stop release of renin.
So, angiotensin II is not formed and release of aldosterone from adrenal cortex is stopped.
3) ACTH hormone mainly stimulates secretion of glucocorticoids. It has only a mild stimulating effect on aldosterone secretion.
Note: Above points no.1 and 2 are known as RAA SYSTEM/ RENIN ANGIOTENSIN MECHANISM/ RAAS MECHANISM/ RENIN ANGIOTENSIN ALDOSTERONE MECHANISM/ RAAS/ RENIN ANGIOTENSIN ALDOSTERONE SYSTEM
GLUCOCORTICOIDS
Glucocorticoids are:
Cortisol
Corticosterone
Cortisone
- Secreted mainly by zona fasciculate of adrenal cortex.
FUNCTIONS OF GLUCOCORTICOIDS
1) Cortisol hormone is Life-protector because, it helps to withstand stress and trauma in life.
2) Glucocorticoids increase Blood glucose level,
- By increasing Gluconeogenesis.
- By inhibiting uptake and utilization of Glucose by peripheral cells.
3) Increase degradation of Proteins,
- By releasing amino acids from body cells (except liver cells), into the blood
- By its absorption from intestine and increasing excretion through urine.
8) Stimulate Bone Resorption (osteoclastic activity) and inhibit Bone Formation & Mineralization (osteoblastic activity).
9) Increase catabolism of proteins in muscle.
10) Decrease number of Eosinophils, Basophils & Lymphocytes.
11) Increase number of Neutrophils, RBCs and Platelets.
12) Essential for the constriction of vessels.
13) Essential for normal functioning of nervous system.
14) Exposure to any type of stress, increases secretion of ACTH, which increases Glucocorticoid secretion.
15) It provides resistance to body against stress.
16) Inhibiting release of chemical substances from damaged tissues
17) Decreases permeability of capillaries.
18) Inhibiting migration of leukocytes into affected area by Suppressing T cells and other Leukocytes.
19) Prevent various reactions in Allergic conditions.
20) Suppress immune system of body by decreasing number of circulating T lymphocytes.
MODE OF ACTION
- Glucocorticoids bind with receptors to form Hormone Receptor Complex
↓
- Which activates DNA to form mRNA.
↓
- mRNA causes synthesis of enzymes, which perform cell function.
REGULATION OF SECRETION
Role of Anterior Pituitary – ACTH
- Anterior pituitary regulates Glucocorticoid secretion by secreting Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH).
- ACTH acts by formation of cyclic AMP.
- ACTH secretion is regulated by hypothalamus through Corticotropin-Releasing Factor (CRF).
- CRF reaches anterior pituitary through Hypothalamo-Hypophyseal portal vessels.
- CRF stimulates Corticotropes of anterior pituitary and causes synthesis and release of ACTH.
- CRF secretion is induced by several factors such as Emotion, Stress, Trauma and Circadian rhythm CRF in turn, causes release of ACTH, which induces Glucocorticoid secretion.
Feedback Control
Cortisol regulates its own secretion through Negative feedback control by inhibiting release of CRF from hypothalamus and ACTH from Anterior pituitary.
Circadian Rhythm of ACTH
Rate of secretion of both ACTH and CRF is high in morning and low in evening.
SEX HORMONES
- Adrenal cortex secretes mainly the male sex hormones, which are called Androgens.
- These Androgens secrets small quantity of Oestrogen/Estrogen and Progesterone hormones.
Androgens secreted by Adrenal cortex are:
Dehydroepiandrosterone
Androstenedione
Testosterone.
- Dehydroepiandrosterone is the most active Adrenal Androgen.
- Androgens, in general, are responsible for masculine features of the body .
- Normally the Adrenal androgens have no significant physiological effects, due to its low amount of secretion in both males and females.
HORMONES OF ADRENAL CORTEX AND MEDULLA











Leave a Reply