
This post contains the whole syllabus of 4th BHMS (theory and practical). This is prepared for the purpose of providing the whole idea of learning objectives in each subject.
This syllabus is applicable from the academic session 2015-2016, as per the guidelines of Central Council of Homoeopathy (India).
Subjects to be taught in 4th BHMS
- PRACTICE OF MEDICINE
- COMMUNITY MEDICINE
- HOMOEOPATHIC MATERIA MEDICA
- ORGANON OF MEDICINE
- HOMOEOPATHIC REPERTORY
If you want to prepare for the university examination you should follow the below mentioned links,
Table of Contents
Toggle4th BHMS PRACTICE OF MEDICINE
Theory syllabus
- Nutritional and metabolic diseases.
- Diseases of haemopoietic system.
- Endocrinal diseases.
- Infectious diseases.
- Diseases of cardiovascular system.
- Diseases of urogenital tract.
- Disease of CNS and peripheral nervous system.
- Psychiatric disorders.
- Diseases of locomotor system (connective tissue, bones and joints disorders)
- Diseases of skin and sexually transmitted diseases.
- Tropical diseases.
- Paediatric disorders.
- Geriatric disorders.
- Applied anatomy and applied physiology of different organ and systems relating to specific diseases.
- Knowledge of clinical examination of respective systems.
General management and homoeopathic therapeutics for all the topics to be covered in 3rd B.H.M.S and 4th B.H.M.S shall be learnt simultaneously and the emphasis shall be on study of man in respect of health, disposition, diathesis, disease, taking all predisposing and precipitating factors, i.e., fundamental cause, maintaining cause and exciting cause.
Study of therapeutics does not mean simply list of specifics for the clinical conditions but learning of applied materia medica which shall be stressed upon.
Practical or clinical syllabus
Each candidate shall submit of twenty complete case records (ten in 3rd B.H.M.S and ten in 4th B.H.M.S).
The examination procedure will include one long case and one short case to be prepared. During clinical training, each student has to be given adequate exposure to,
- Comprehensive case taking following Hahnemann ‘s instructions;
- Physical examinations (general, systemic and regional);
- Laboratory investigations required for diagnosis of disease conditions;
- Differential diagnosis, provisional diagnosis and interpretation of Investigation reports;
- Selection of similimum and general management.
4th BHMS COMMUNITY MEDICINE SYLLABUS
Theory syllabus
- Epidemiology
- Principles and methods of epidemiology.
- Epidemiology of communicable diseases: general principles of prevention and control of communicable diseases;
- Communicable diseases: their description, mode of spread and method of prevention.
- Protozoan and helminthic infections: life cycle of protozoa and helminths, their prevention.
- Epidemiology of non-communicable diseases: general principles of prevention and control of non- communicable diseases.
- Screening of diseases.
- Bio-statistics
- Need of biostatistics in medicine
- Elementary statistical methods
- Sample size calculation
- Sampling methods
- Test of significance
- Presentation of data
- Vital statistics
- Demography and family planning; population control; contraceptive practices.
- National family planning programme.
- Health education and health communication
- Health care of community.
- International health
- Mental health
- Maternal and child health
- School health services
- National health programs of India including Rashtriya Bal Chikitsa Karyakram.
- Hospital waste management
- Disaster management
- Study of aphorisms of organon of medicine and other homoeopathic literatures, relevant to above topics including prophylaxis.
Practical syllabus
- Food additives; food fortification, food adulteration; food toxicants
- Balanced diet
- Survey of nutritional status of school children, pollution and water purification
- Medical entomology
- Family planning and contraception
- Demography
- Disinfection
- Insecticides
Field Visits
- Milk dairy
- Primary Health Centre (PHC)
- Infectious diseases hospital
- Industrial unit
- Sewage treatment plant
- Water purification plant
Note:
Students are to maintain practical records or journals in support of above practical or field visits.
Reports of the above field visits are to be submitted by the students.
Each student has to maintain records of at least ten infectious diseases.
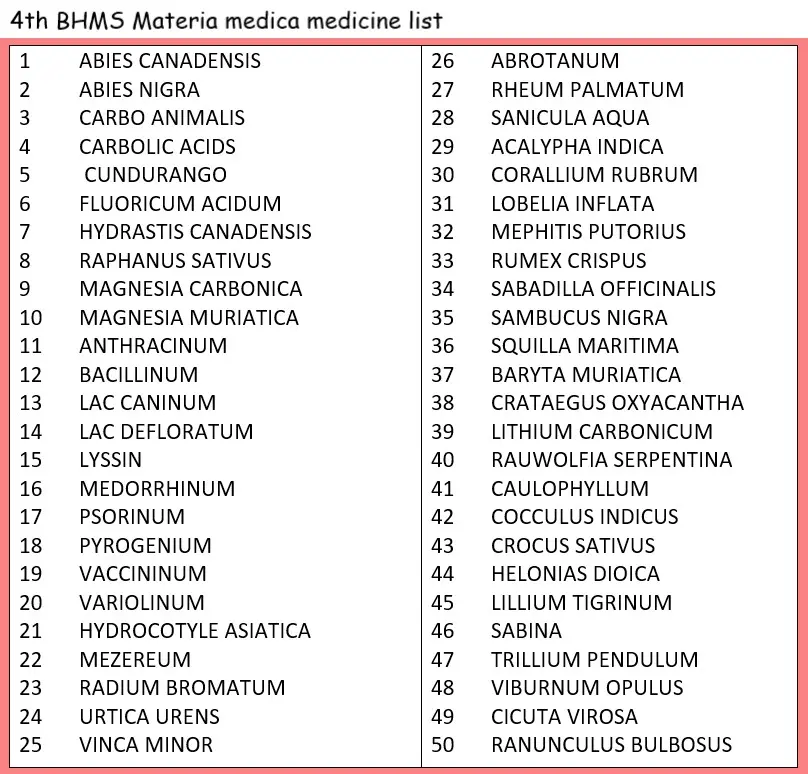
4th BHMS MATERIA MEDICA SYLLABUS
In addition to the syllabus of First, Second and Third BHMS including the medicines, the following additional topics and medicines are included in the syllabus for the Fourth BHMS examination.
- General topics of Homoeopathic Materia medica – Sarcodes – definition and general indications.
- Medicines listed in 4th BHMS shall be learnt in relation to the medicines of 3rd and 4th BHMS for comparison wherever required.
HERE IS A COMPLETE LIST OF HOMOEOPATHIC MEDICINES SO YOU CAN EASILY LEARN EACH OF THEM – A TO Z MEDICINES OF HOMOEOPATHIC MATERIA MEDICA

Practical or clinical syllabus
Each student shall maintain a journal having record of ten acute and ten chronic case takings.
4th BHMS ORGANON OF MEDICINE SYLLABUS
Theory syllabus
In addition to the syllabus of First B.H.M.S, Second B.H.M.S and Third B.H.M.S, the following shall be covered,
- Evolution of medical practice of the ancients (Prehistoric Medicine, Greek Medicine, Chinese medicine, Hindu medicine and Renaissance) and tracing the empirical, rationalistic and vitalist thoughts.
- Revision of Hahnemann ‘s Organon of Medicine (Aphorisms 1-294) including footnotes (5th & 6th Editions translated by R.E. Dudgeon and W. Boericke).
- Homoeopathic Philosophy from philosophy books of,
- Stuart Close (Chapters- 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 17),
- J. T. Kent (Chapters – 18 to 22)
- A. Roberts (Chapters- 1 to 5, 20, 22 to 33, 35)
- Richard Hughes (Chapters- 1 to 10)
- Dunham (Chapters- 1 to 7).
- Chronic Diseases:
- Hahnemann ‘s Theory of Chronic Diseases.
- H. Allen ‘s The Chronic Miasms – Psora and Pseudo-psora; Sycosis
Emphasis should be given on the way in which each miasmatic state evolves and the characteristic expressions are manifested at various levels and attempt should be made to impart a clear understanding of Hahnemann ‘s theory of chronic miasms.
The characteristics of the miasms need to be explained in the light of knowledge acquired from different branches of medicine.
Learn the therapeutic implications of theory of chronic miasms in practice and this will entail a comprehension of evolution of natural disease from miasmatic angle, and it shall be correlated with applied materia medica.
Practical or clinical syllabus
The students shall maintain practical records of patients treated in the outpatient department and inpatient department of the attached hospital.
The following shall be stressed upon in the case records, namely;
- Receiving the case properly (case taking) without distortion of the of patient ‘s expressions;
- Nosological diagnosis;
- Analysis and evaluation of the symptoms, miasmatic diagnosis and portraying the totality of symptoms;
- Individualisation of the case for determination of the similimum, prognosis, general management including diet and necessary restrictions on mode of life of the individual patients;
- State of susceptibility to formulate comprehensive plan of treatment;
- Order of evaluation of the characteristic features of the case would become stepping stone for the Repertorial totality;
- Remedy selection and posology;
- Second prescription.
Note:
- Each student has to maintain records of twenty thoroughly worked out cases (ten chronic and ten acute cases).
- Each student shall present at least one case in the departmental symposium or seminar.
4th BHMS REPERTORY SYLLABUS
Theory syllabus
- Comparative study of different repertories (like Kent ‘s Repertory, Boenninghausen ‘s Therapeutic Pocket Book and Boger- Boenninghausen ‘s Charactetristic Repertories, A Synoptic Key to Materia Medica).
- Card repertories and other mechanical aided repertories– History, Types and Use.
- Concordance repertories (Gentry and Knerr)
- Clinical repertories (William Boericke etc.)
- An introduction to modern thematic repertories- (Synthetic, Synthesis and Complete Repertory and Murphy ‘s repertory)
- Regional repertories
- Role of computers in repertorisation and different software.
Practical or clinical syllabus
Students shall maintain the following records, namely;
- Five acute and five chronic cases (each of medicine, surgery and obstetrics and gynaecology) using Kent ‘s Repertory
- Five cases (pertaining to medicine) using Boenninghausen ‘s therapeutics pocket book.
- Five cases (pertaining to medicine) using Boger-Boenninghausen ‘s characteristics repertory.
- Five cases to be cross checked on repertories using homoeopathic software.

Where is materia Medica
Materia medica syllabus is also mentioned in this post.
Superb work mam.