Urea, also known as carbamide, is a compound commonly found in urine and plays a crucial role in the body’s nitrogen metabolism.
In homeopathy, urea is used medicinally to address various conditions such as tuberculosis, renal dropsy, gouty eczema, and diabetes.
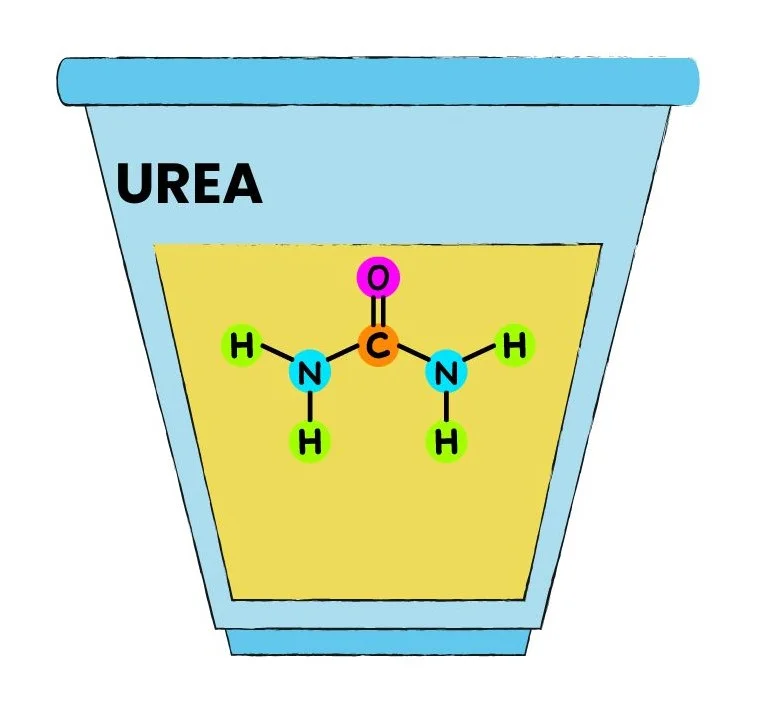
Table of Contents
ToggleSOURCE INFORMATION
- Chemical compound
- Chemical Formula: CO(NH2)2
- Urea is a naturally occurring compound found in the urine of mammals, including humans.
- In homeopathy, it is typically prepared from synthetic sources.
Interesting Facts
- Urea was first synthesized in 1828 by Friedrich Wöhler, marking a significant milestone in organic chemistry as it was the first organic compound to be artificially synthesized from inorganic materials.
- In addition to its medicinal uses in homeopathy, urea is widely used in various industries, including agriculture, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals.
DRUG PATHOGENESIS
- Urea exerts its medicinal effects primarily on the urinary system and metabolic processes.
- It is indicated for conditions such as tuberculosis, renal dropsy, gouty eczema, albuminuria, diabetes, and uraemia.
- Urea acts as a hydrogogue diuretic, promoting the production and excretion of urine, which can be beneficial in the treatment of dropsies.
CHIEF GUIDING SYMPTOMS
- Affinity for the Urinary System and Metabolic Disorders: Urea exhibits a specific affinity for addressing urinary system disorders and metabolic imbalances.
- Indicated Conditions: Tuberculosis, Enlarged Glands, Renal Dropsy, Gouty Eczema: Urea is indicated for treating tuberculosis-related symptoms such as lumps and enlarged glands, as well as conditions like renal dropsy and gouty eczema.
- Urine Characteristics: Thin Urine of Low Specific Gravity, Albuminuria: Urea is associated with urine that is thin and of low specific gravity, often accompanied by the presence of albumin (albuminuria).
- Hydrogogue Diuretic Action: Urea acts as a hydrogogue diuretic, aiding in the elimination of excess fluid from the body, making it valuable in addressing dropsical conditions like renal dropsy.
RELATIONSHIP WITH OTHER DRUGS
- Uric Acid: Similarities with Urea in treating gout, gouty eczema, rheumatism, and lipoma.
- Urinum: Comparable to Urea in addressing acne, boils, scurvy, and dropsy.
- Urtica: Potential similarities with Urea in certain urinary and skin-related symptoms.
- Tuberculinum: Possible parallels with Urea, especially in tuberculosis-related symptoms.
- Thyroidinum: Likely resemblances with Urea in managing metabolic and glandular disorders.
DOSE
- The recommended dose of urea is 10 grains every 6 hours.
- It is important to consult with a qualified homeopathic practitioner for individualized dosage instructions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary indications for using urea in homeopathy?
- Urea is primarily indicated for conditions such as tuberculosis, renal dropsy, gouty eczema, albuminuria, diabetes, and uraemia.
What is the origin of urea used in homeopathy?
- Urea used in homeopathy is typically prepared from synthetic sources rather than being derived from natural sources like urine.
Is urea safe to use with other medications?
- Urea does not have specific known interactions with other drugs.
- However, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before combining it with other medications.
Meaning of Difficult Words
- Tuberculosis: A bacterial infection that primarily affects the lungs but can also affect other parts of the body.
- Dropsy: An old term for oedema or swelling, typically due to the accumulation of fluid in the body’s tissues.
- Hydrogogue: A diuretic agent that promotes the excretion of large amounts of urine.
- Albuminuria: The presence of albumin, a protein, in the urine, often indicating kidney damage.
- Uraemia: A condition characterized by high levels of urea and other waste products in the blood, typically due to kidney dysfunction.












Leave a Reply