If you or someone you know has diabetes, you may have heard about insulin and how it helps to manage blood sugar levels.
But have you ever wondered how people actually take insulin? That’s where the insulin syringe comes in! In this guide, we’ll explore what an insulin syringe is, how it works, and how to use it safely.
Table of Contents
ToggleWHAT IS AN INSULIN SYRINGE?
An insulin syringe is a special type of needle and tube used to give insulin injections.
Insulin is a hormone that helps the body to use sugar for energy.
People with diabetes sometimes need insulin injections to keep their blood sugar levels in check.
The insulin syringe is designed to make it easy to measure and give the right amount of insulin.
PARTS OF AN INSULIN SYRINGE
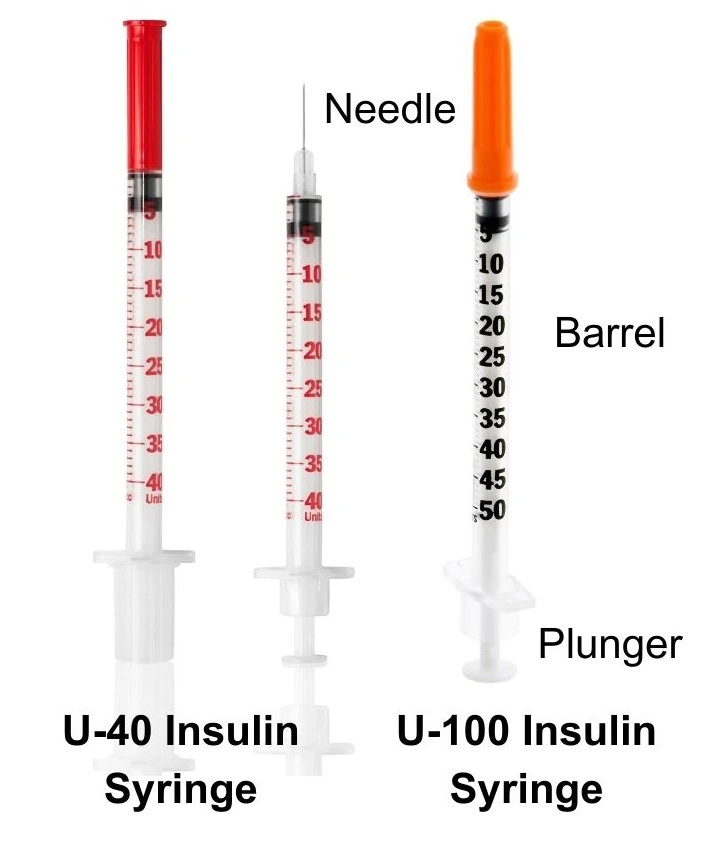
An insulin syringe has a few important parts:
- The Barrel: This is the main part of the syringe, like a tiny tube where the insulin goes.
- The Plunger: The plunger is like a stick inside the barrel. It helps push the insulin out when you give the injection.
- The Needle: The needle is a thin, sharp metal point at the end of the syringe. It’s what goes under the skin to deliver the insulin.
TYPES OF INSULIN SYRINGE AND THEIR USES
There are two main types of insulin syringes:
U-100 Insulin Syringe
This type is used with most common types of insulin. Each milliliter (mL) of this insulin has 100 tiny units.
The syringe is color-coded orange.
U-40 Insulin Syringe
This type is used with a less common type of insulin. Each mL of this insulin has 40 units.
The syringe is color-coded red.
Make sure to use the right syringe for the type of insulin you are prescribed!
SIZES OF INSULIN SYRINGE
Insulin syringes come in various sizes, and choosing the right size is crucial for accurate insulin dosing and ease of administration.
The size of an insulin syringe is determined by its volume capacity, usually measured in milliliters (mL).
Different syringe sizes are available to accommodate various insulin dosages, making it easier for individuals with diabetes to administer the correct amount of insulin.
Common insulin syringe sizes include:
0.3 mL Insulin Syringe
This is the smallest insulin syringe size, typically designed for people who require very small insulin doses.
It is commonly used with U-100 insulin, where 1 mL of insulin contains 100 units.
These syringes are marked with clear calibrations to allow precise measurement of tiny insulin doses.
0.5 mL Insulin Syringe
This size is slightly larger than the 0.3 mL syringe and is also used for smaller insulin doses.
Like the 0.3 mL syringe, it is commonly used with U-100 insulin.
1.0 mL Insulin Syringe
The 1.0 mL syringe is the most common insulin syringe size and is suitable for individuals who require larger insulin doses.
Like the other syringe sizes, it is calibrated for U-100 insulin, making it easy to measure doses accurately.
1.5 mL Insulin Syringe
This size is less common but may be available in certain regions or for specific insulin types.
It is also calibrated for U-100 insulin.
2.0 mL Insulin Syringe
Similar to the 1.5 mL syringe, the 2.0 mL syringe is less commonly used but may be available for certain insulin formulations.
Factors that influence the choice of syringe size include the individual’s insulin requirements, the concentration of the prescribed insulin (U-100 or U-40), and the ease of use based on individual preferences.
Some important considerations when choosing an insulin syringe size include:
Insulin Concentration
Ensure that the syringe is calibrated for the specific concentration of insulin prescribed by your physician (U-100 or U-40).
Using the wrong syringe size for the insulin concentration can lead to incorrect dosing.
Insulin Dosage
Choose a syringe size that can accommodate the required insulin dose without leaving too much empty space in the syringe.
It is generally recommended to select a syringe that can hold slightly more insulin than the prescribed dose to compensate for any air bubbles during filling.
Needle Length
The length of the needle on the syringe can also vary.
Shorter needles are often preferred for individuals who are lean or have less body fat, while longer needles may be more suitable for those with more body fat.
Ease of Handling
Some individuals may find it easier to handle larger syringes, while others may prefer smaller ones.
Comfort and ease of use are important factors to consider when selecting an insulin syringe size.
Comfortability and Adherence
The chosen syringe size should encourage comfortability with insulin administration and adherence to the prescribed insulin regimen.
NOTE:
Remember, using the correct insulin syringe size is essential for accurate dosing and proper diabetes management. Always consult with a healthcare professional for guidance on the appropriate syringe size and insulin administration techniques based on individual needs and medical requirements.
HOW TO USE AN INSULIN SYRINGE
Using an insulin syringe might sound a bit tricky at first, but with practice, it becomes easier. Here are the steps to use one:
Step 1: Wash Hands
Before you touch anything, wash your hands with soap and water. Clean hands help prevent infections.
Step 2: Get the Insulin Ready
- Check the insulin bottle to make sure it’s the right one your doctor prescribed.
- If the insulin looks cloudy, gently roll the bottle between your hands. But don’t shake it!
- Clean the top of the insulin bottle with an alcohol swab.
Step 3: Assemble the Syringe
- Take the syringe out of its package, being careful not to touch the needle or plunger.
- Put the needle on the end of the syringe.
- Take off the needle’s cap, being careful not to touch the needle.
Step 4: Draw the Insulin
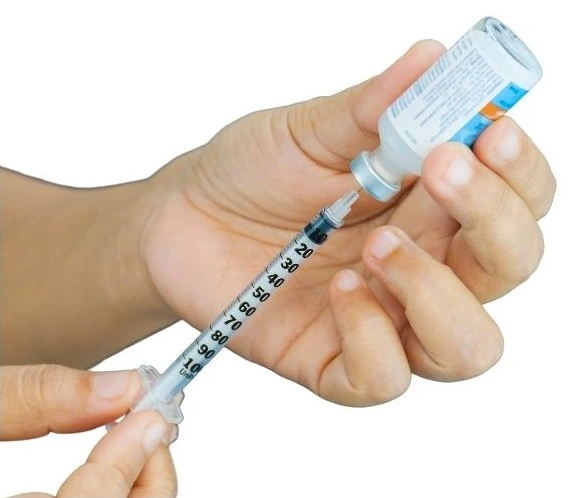
- Stick the needle into the top of the insulin bottle.
- Turn the bottle and syringe upside down.
- Slowly pull back the plunger to fill the syringe with the right amount of insulin.
- Check for air bubbles in the syringe. If you see any, tap the syringe gently to make the bubbles go away.
Step 5: Measure the Dose
Look at the numbers on the side of the syringe. Make sure you have the right amount of insulin in the syringe.
Step 6: Give the Injection
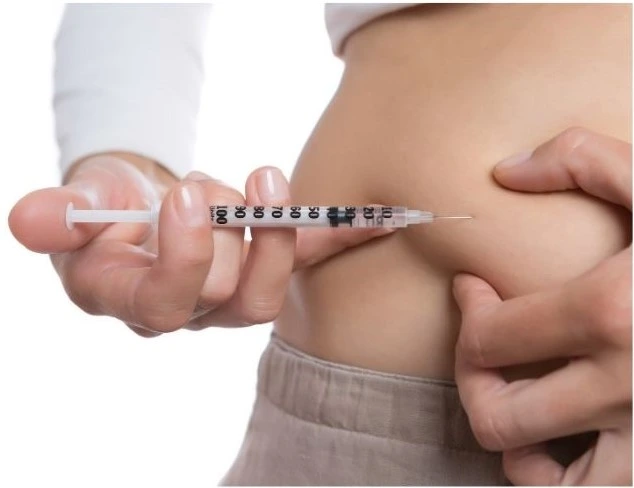
- Choose where you want to give the injection – like your tummy, thigh, or upper arm.
- Clean the spot with an alcohol swab and let it dry.
- Pinch the skin a little to make a tiny fold.
- Put the needle into the skin quickly, at a 90-degree angle for most people, or a smaller angle for kids or people with less body fat.
- Push the plunger all the way down to give the insulin.
- Take the needle out and press on the spot with a cotton ball or tissue.
Step 7: Throw Away the Syringe
After using the syringe, take the needle off and throw it in a special sharp’s container. Never put used syringes or needles in the regular trash!
TIPS FOR OPTIMAL INSULIN SYRINGE USE
- Always follow your doctor’s instructions for taking insulin, including the dose and type of insulin.
- Change where you give the injections to keep your skin healthy.
- Don’t reuse syringes or needles – always use a new one for each injection.
- Keep your insulin and syringes away from the sun and extreme heat or cold.
CONCLUSION
The insulin syringe is a tiny but essential tool for people with diabetes.
By following the steps and tips in this guide, you can use the syringe safely and manage your diabetes like a pro!
Always talk to your doctor or nurse if you have any questions or need help.
LEARN HOW TO DISPOSE INSULIN SYRINGE IN RESPONSIBLE WAY.
DO YOU KNOW HOW TO CALCULATE INSULIN DOSAGE?
With practice, taking insulin becomes just another part of your day, helping you stay healthy and feeling great!













Leave a Reply