
This post is about two celebrated microbiologist whose discoveries cause the beginning of new era in the field of microbiology, they are Louis Pasteur & Robert Koch.
Table of Contents
ToggleLOUIS PASTEUR (1822-1895)

For hundreds of years doctors kept trying to understand the causes of diseases.
In mid-19th century, people believed that diseases were caused by polluted air to which they called Miasma.
The actual evolution in medical history started not by a physician, but by a chemist whose name was Louis Pasteur.
Who was Louis Pasteur?
He was a French chemist working as a teacher in a university.
In 1857 he was being asked by a wine company to find out the reasons for wine turned sour after being prepared.
He did research using microscope and found out that there were germs in the air that could cause liquors to go sour or decompose.
So, what did he do next?
- He developed a process to kill the germs by boiling the wine and then cooling it down and named the process “Pasteurisation”.
- He observed that germs came from the air and that’s why they can be prevented from entering the liquid in first place.
- He proved that by sealing a quantity of liquid in an airtight swan necked flask and leaving another quantity exposed to air.
- On the basis of these experiments he published his Germ theory in 1861.
- Pasteur used his germ theory to treat diseases.
- It came to his knowledge that British Dr. Edward Jenner had developed a vaccination against small pox disease.
- Pasteur believed that germ theory could help to understand that how vaccination worked.
- So, he took the blood samples of healthy person and compared them with the blood of persons with various diseases.
- He found out that blood of diseased person was containing lots of germs.
Discoveries by Pasteur
- Pasteurisation process is still being used in most of the dairy products.
- He developed vaccinations for Chickenpox, Cholera, Diphtheria, and Rabies.
- He recommended to boil the surgical instruments before operation to kill any germs on them.
- Pasteur’s discoveries were a revolution in medical history to understand the relation between germs and diseases.
- Later this led the way for Robert Koch to discover that each disease was caused by some specific organisms which are known as “KOCH’S POSTULATES”.
Before we dig more in history let’s summarize the discoveries of Louis Pasteur:
- 1861- Pasteur published the Germ theory.
- 1880- Pasteur & Chamberland immunised chickens against cholera.
- 1881- Inoculation (immunization) of sheep against anthrax.
- 1884- Development of vaccination for Rabis.
- 1888- The French government started Pasteur Institute in Paris.
ROBERT KOCH (1843- 1910)

Who was Robert Koch?
- Heinrich Hermann Robert Koch was a German physician & microbiologist.
- A founder of modern bacteriology.
- In 1872 he studied Louis Pasteur’s work and started to research about microorganisms causing diseases in humans and animals.
- In 1876 he invented a procedure to explain that the bacterium Bacillus anthracis were the cause for the disease anthrax in animals that can be passed on in humans too.
- That was the first time in history that a particular organism was proved to be the cause of a particular disease.
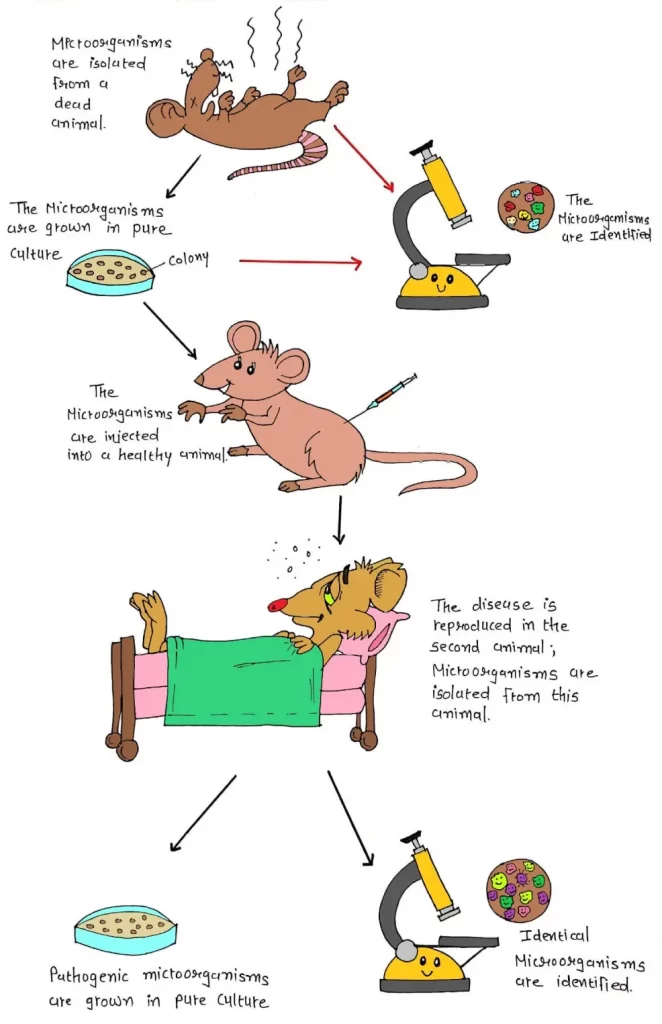
Koch extracted anthrax bacillus from an infected sheep and injected it into a mouse and allowed it to grow.
Then he extracted the bacterium from the blood of that mouse and injected it into another mouse and repeated this process through 20 generations of mouse before he got confirmed that he had isolated the bacteria which caused anthrax.
What made him so prominent?
- The methods developed by him became the standard methods used by scientists for accurate results.
- 1878 he discovered that microbes cause wounds to go septic.
- He stained the microbes with dye, made it possible to take photographs under microscope.
- Due to this method he was able to study microbes more precisely and proved that every disease was caused by a different germ.
- In 1882 he identified the organisms that caused tuberculosis.
- In 1883 he did find out the causative organisms for cholera.
- He discovered through careful research and observation with the help of microscope, photography and dyes.
- Due to his research work, in 1891 the German government set up an ‘Institute of Infectious Diseases’ in Berlin-Mitte.
- In 1905 Koch was awarded the Noble prize for his work in microbiology.
Koch’s postulates
- Postulate means a requirement or prerequisite.
- Koch gave 4 criteria to establish a causative relationship between a microbe and a disease.
- The same pathogen must be present in every case of the disease.
- The pathogen must be isolated from diseased organisms and grown in pure culture.
- When these cultured pathogens are injected into a healthy organism, they should cause the same disease.
- The pathogens must be isolated from the immunized laboratory animals and must be exposed to the original organism.
Exceptions to Koch’s postulates
- Many healthy people carry pathogens but do not express disease symptoms.
- Some microbes are very difficult or impossible to grow in vitro (in the laboratory) in artificial media e.g. Treponema pallidum.
- Many species are species specific. E.g. Brucella abortus cause abortion in animals but no such report in humans.
- Certain diseases develop only when an opportunistic pathogen invades immunocompromised host.
Let’s summarize the main events in Koch’s discoveries.
- 1876 Discovered the causative organism for anthrax.
- 1878 Discovered that microbes cause sepsis of wounds.
- 1882 Identified the causative organism for tuberculosis.
- 1883 Find out the cause of cholera.
- 1891 The German government set up the institute to carry research and development.
- 1905 Won the Noble prize.

Thanks for summarising this whole lot of knowledge into simple article a
Happy to help…keep reading.