In this post you can learn one of the most discussed topic especially among the students “LOGIC IN HOMOEOPATHY“.
There are so many explanations available on this topic from different different authors.
I have tried to explain it in the most possible simple way so, every student can easily understand and remember (for exam).
WORD MEANING
Logic is the Greek word which is derived from “Logos”, which means reason, idea or principle as the expression of thought.
In other words, Logic means the “Science of correct reasoning”.
DEFINITION
There are several definitions of logic that has been suggested.
AMULD- “The science of understanding in the pursuit of truth”.
WHATELY- “The art and science of reasoning”.
THOMSON- “The science of the thought”.
ALDARICH- “The art of reasoning”.
HAMILTON- “The science of the formal laws of thought”.
The word reasoning means to conclude rationally. It helps us to reach the judgement.
Logic is concerned with series of statements to establish a definite theory.
When we try to convince over something, we use an argument.
We give reasons to support a conclusion.
Parts of arguments are-
PREMISES– Theories taken as the base or support.
CONCLUSIONS– The theories being proved or supported.
TYPES OF LOGIC
Logic can be classified mainly into two types.
- INDUCTIVE LOGIC
- DEDUCTIVE LOGIC
There are also other types of logic like Mathematical logic, Symbolic logic, Informal logic, Formal logic, Abductive logic etc.
Table of Contents
ToggleINDUCTIVE LOGIC
The word “To induce” means leading to do something or make someone to do something.
Lord Francis Bacon (father of inductive logic) originated this method of induction and stated in his Novum Organum.
DEFINITION
It is the process of drawing a conclusion by observing a pattern in specific case.
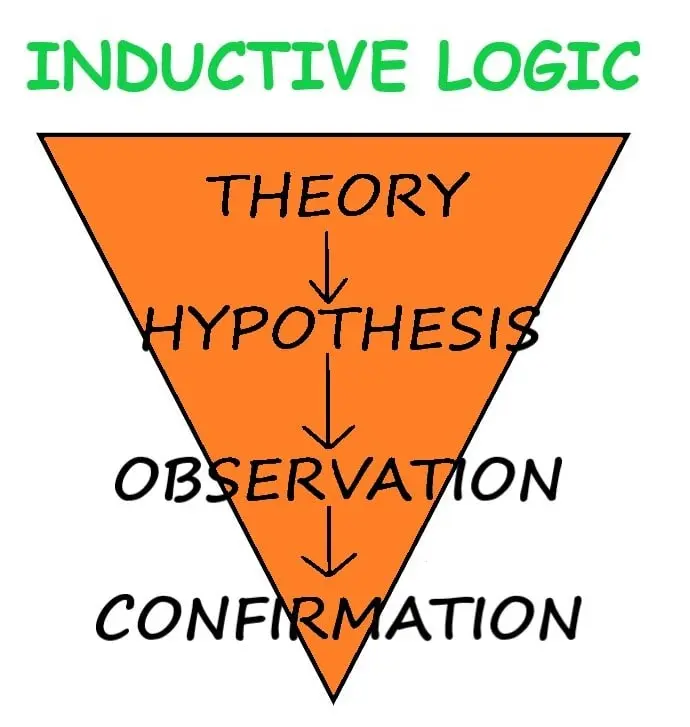
By inductive logic, from a number of observations a general conclusion is drawn.
Inductive reasoning is one of the most frequently used method in thinking.
It is commonly mentioned as “Generalizing” because it means that one begins with specific details and progresses to a general principle as a conclusion.
A generalization is a broad statement about a group of people or things.
It suggests that something they have in common.
Inductive reasoning makes broad generalization from specific observation.
We go from the specific to the general.
Utility of inductive reasoning
- It provides freedom to investigate.
- It provides freedom to study the nature.
- It provides freedom to draw conclusion individually.
What do we do in inductive reasoning?
FIRST, WE MAKE MANY OBSERVATIONS
↓
THEN WE TRY TO RECOGNIZE A PATTERN
↓
CONCLUDE A GENERALIZATION
↓
FIGURE OUT AN EXPLANATION
So, now we can understand that inductive logic requires,
- Accurate observations
- Precise interpretation of the observed reality
- Reasonable explanation
- Scientific conclusion
Accurate observations
- The word accurate means correct or exact in all details.
- The word observation means to notice or perceive something.
- In short, this method suggests to perceive minute details.
Precise interpretation of the observed reality
- Precise means accuracy of expression or free from error.
- Interpretation is the action of explaining the meaning of something.
- Reality is the state or quality of having existence.
- In short, interpretation of the collected information should be free from error.
Reasonable explanation
- The word reasonable stands for comfortable or agreeable to understand.
- Explanation means to clarify in more details.
- In short, facts should be clarified in detail on agreeable ground.
Scientific conclusion
- The scientific conclusion we reach should be aggregable with the reality we observed.
Examples
- Every Rabbit in a random sample of 5000 Rabbit is white.
this supports the conclusion that: All Rabbits are white. - John is an intelligent student; he is a medical student.
Joseph is an intelligent student who is also studying medicine.
Andrea is an intelligent student and she is also a medical student.
Conclusion: All the medical students might be intelligent.
DEDUCTIVE LOGIC
The word deduce is a Latin derivative which means “To lead”.
Deduction is the action or process of abstracting something.
Deductive reasoning is the exact opposite of inductive reasoning.
Here, we draw a particular conclusion from a universal or general premise.
This means, if the universal or general premises is true, then a particular conclusion derived from this premise must also be true.
DEFINITION
It is the application of a general theory to a specific case.
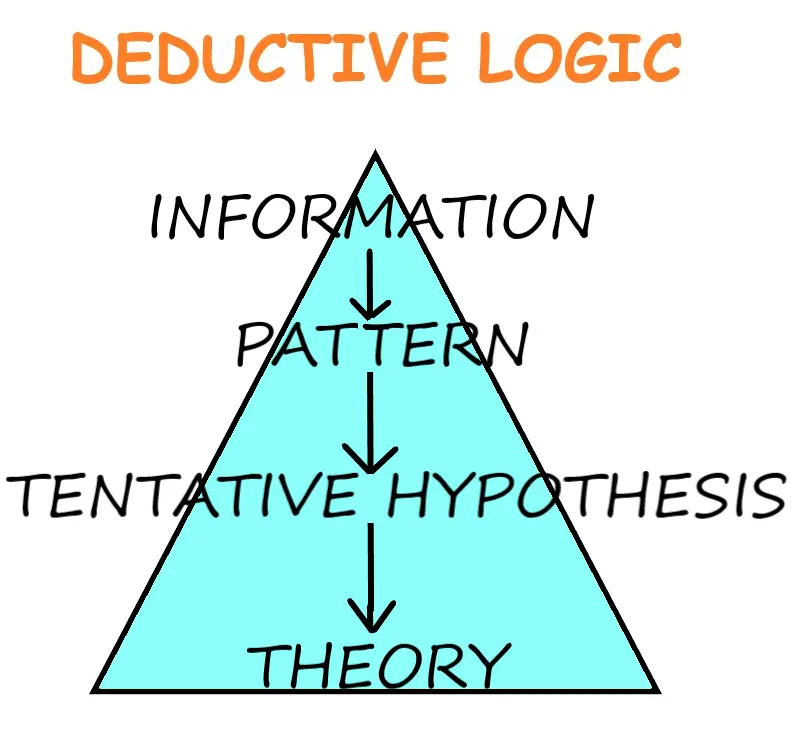
Utility of deductive reasoning
It is a scientific method of proving a Hypothesis or Theory based on reasoning.
What do we do in deductive reasoning?
FIRST, WE OBSERVE FROM AVAILABLE FACTS, INFORMATION OR KNOWLEDGE
↓
WE USE THEM AS THE BASE
↓
WE DRAW A VALID (AGREEABLE) STATEMENT (HYPOTHESIS)
↓
WE FORM AN EFFECTIVE CONCLUSION.
Examples
• All the Rabbits are white. We have a random sample of Rabbits.
Conclusion: all the Rabbits in sample must be white.
• All the medical students are intelligent and john is a medical student.
Conclusion: John is intelligent because he is a medical student.
APPLICATION OF LOGIC IN HOMOEOPATHY
Homoeopathy is a therapeutic system of medicine which was found and constructed on the basis of logical principles.
To understand this, we should examine the earlier steps adopted by Dr. Samuel Hahnemann in order to heal the diseased person through the logical application of natural laws.
The analysis of organon of medicine and homoeopathic Materia medica clearly suggests that homoeopathy is a product of inductive logic.
Let’s try to understand the application of logic to some of the principles of homoeopathy.
LAW OF SIMILAR
In 1790, Dr. Hahnemann while translating Dr. William Cullen’s A Treatise on Materia Medica from English to German, he was dissatisfied with an explanation in it, that
“Curative power of Peruvian bark (cinchona bark) can cure the intermittent fever (malaria)”.
Dr. Hahnemann took 4 drams of cinchona extract twice daily for several days and he observed the development of malaria like symptoms.
↓
He observed a pattern that, disease curing property of a medicinal substance can produce disease like symptoms if they are taken by healthy individuals.
↓
- He repeated the same experiment on himself to confirm before coming to final conclusion.
- He conducted similar experiments on his friends and other volunteers (generalization).
- As he expected, all of them had the same symptoms like malaria fever.
↓
These experiments led him to an old therapeutic saying,
“Similia Similibus Curanter” which means, “Like Cures Like”.
DOCTRINE OF DRUG PROVING
Dr. Hahnemann and other pioneers of homoeopathy proved each single remedy to know their disease producing power on various healthy provers.
↓
They collected common and peculiar characteristics
↓
They considered the disease producing property of remedies as disease curing property.
Thus, doctrine of drug proving is the method of inductive reasoning.
THE HOLISTIC APPROACH
The philosophical meaning of holistic is the belief that the parts of something are intimately interconnected and explained only as a whole.
Homoeopathy believes that vital force (dynamic power) animates the internal material organisms.
Derangement of this vital force affects the person as a whole, this person expresses his derangement in the form of different sign and symptoms on physical, mental or emotional plane.
When we integrate all these signs and symptoms, it represents the person as a whole.
In this way, the holistic approach of homoeopathy clearly indicated the application of inductive logic.













This is very helpful.
simple and good explanation
Thanks…