
HISTORY OF MEDICINE PART 2 is the continuation of the previous post, HISTORY OF MEDICINE PART 1 where the first half of this post is covered.
Here, we will continue our learning about the History of ancient medicine.
So, let’s revise the timeline which we already discussed in the first part of this post.
[Note: Words with (*) are particularly defined at the end of this post.]
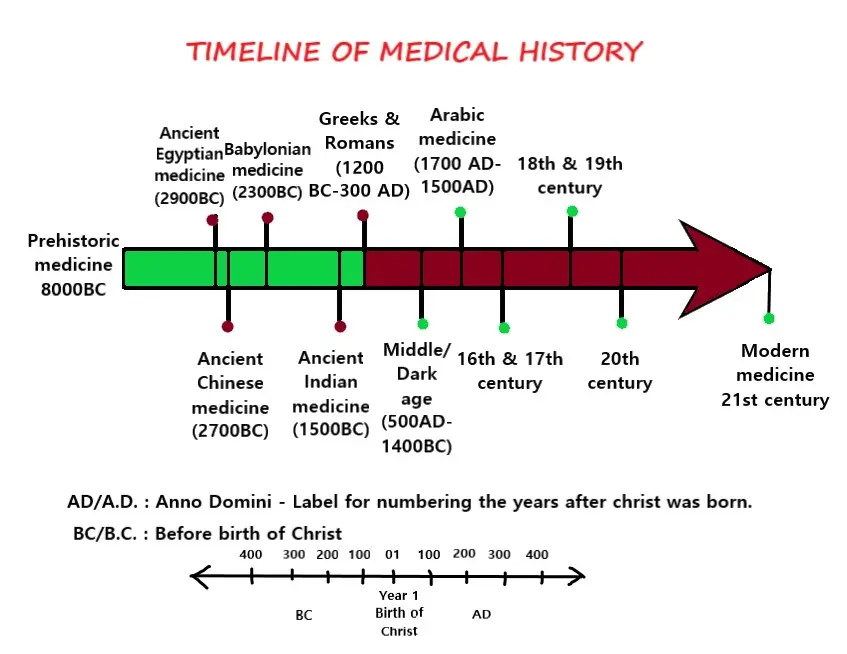
So now you can understand by the image, it can be listed as below
1) Prehistoric medicine (8000 BC)
2) Ancient Egyptian medicine (2900 BC)
3) Ancient Chinese medicine (2700 BC)
4) Mesopotamian/ Babylonian medicine (2300 BC)
5) Ancient Indian medicine (1500 BC)
6) Greek and Romans (1200 BC- 300 AD)
7) Middle age/ dark age (500 AD- 1400 BC)
8) Islamic/ Arabic medicine (700 AD-1500 AD)
9) The Renaissance(rebirth) period/ 16th & 17th Century
10) Modern medicine/ 18th & 19th century
11) Modern medicine/ 20th century
12) 21st century
Table of Contents
Toggle7.MIDDLE AGE/ DARK AGE MEDICINE (500 AD-1400 BC)

- The fall of Roman empire.
- The people in Europe were not able to get clean drinking water, regular bathing or sewage system.
- So, there was poor public hygiene & congested living condition.
- Starvation and diseases were common.
RELIGIOUS INFLUENCE
- Usually priests & religious scholars were physicians.
BELIEFS
- Diseases were punishments of gods for sins.
TREATMENTS
- Only was to pray Gods for forgiveness.
- Hospitals were in monasteries* or other religious households.
- Religious staff (sisters) were giving food or comfort.
- To cure illness, nothing else were done.
- Using herbal remedies, potions or traditional cure were seen as witchcraft & banned by church.
BIGGEST CHALLENGE
- Bubonic plague/ black death broke out in Istanbul.
- Very soon traders carried disease throughout the Europe.
- In some areas it killed 90% of the population (49 million people died).
SUMMARY
- Fall of roman empire.
- People were starving & suffered from diseases due to poor living habits.
- Medicine system dominated by church.
- Treatment was only to pray for mercy.
- Traditional ways of treatment were banned by church.
- Breakout of bubonic plague killed mass of population.
8.ISLAMIC/ ARABIC MEDICINE (700 AD-1500 AD)

- Texts from Greece & Rome were translated into Arabic language & studied by Islamic scholars.
- They had medical schools in Cairo, Damascus, & Baghdad.
- They treated rich and poor equally.
- Avicenna/ Abu Ali Sina/ Pur Sina– Father of modern medicine.
- Az Zahrawi- Greatest surgeon of middle ages & father of surgery.
- They diagnosed the diseases based upon 6 principles.
- Nature of the person
- Nature of his/her excreta
- Nature of pain
- Site of swelling
- Type of swelling
- Discharges of body
- They began to use- Medicinal herbs, Diet regulations & Exercises to treat their patients.
- Due to religious reasons they restricted from dissecting bodies so, Anatomy & Surgery were neglected.
- Chemistry and pharmacology were encouraged in Arab countries.
- They became skilled in plants and mineral medicine preparations.
- Words like Drugs, Alcohol, Syrup, Sugar etc. are Arabic origins.
- They used Alcohol to clean the wounds.
- They used Narcotics for Anesthesia.
- Muslim physicians performed very different surgeries like removal of kidney stones or Varicose veins, or Replacement of dislocated joints.
SUMMARY
- Greek and Roman texts were translated in Arabic language.
- They had medical schools.
- Diagnosis were made on the basis of 6 principles.
- They were good Chemists & Pharmacologists.
- Words- Drugs, Alcohol, Syrup, Sugar are Arabic origin.
- They performed different surgeries.
9.RENAISSANCE PERIOD/ 16th And 17th CENTURY MEDICINE

- Starts from the date of discovery of America by Christopher Columbus.
- They studied translated books from Arabic medicine.
- They neglected the study of quality because the quality of substance is difficult to measure.
- Even biologists started to believe that the material(body) is the only truth.
- They ignored the fact of existence of LIFE FORCE inside the material body.
- Medical research was intensified.
- They started studying anatomy in scientific & systemic way.
- Leonardo-da-Vinci & Andreas Vesalius dissected human bodies and made first anatomical drawings.
- They used bodies of criminals and sinners because church did not permit the dissection of God-fearing bodies.
- Discovery of Blood circulation.
- Invention of Microscope (1609).
- Invention of Mercury Thermometer (1714).
SUMMARY
- Intensified medical revolution.
- Study of anatomy and dissection of bodies.
- Belief- material body is the only truth.
- Neglection of existence of life force in body.
- Discovery of microscope, thermometer and blood circulation.
10.MODERN MEDICINE/ 18th And 19th CENTURY

- Control of church authority over medicine had completely faded away.
- Cruel treatment methods like Bloodletting*, Venesections*, Mustard plasters*, Shotgun prescriptions*, Leeches’ applications* and various other methods were freely used by physicians.
- On other hand, Anatomy & Physiology developed very nicely.
- Morgagni’s experiments proved that diseases are the result of pathological changes in tissues and organs.
- But he forgot to discover that why these changes took place in previously healthy tissues?
- In later years, Dr. Samuel Hahnemann made a criticizing note on different medical schools of 18th century.
- By the end of 18th century 3 major group of physicians existed.
- Dogmatists– (Dogma: blind belief), rationalists who believed we cannot cure disease until we know it’s cause.
- Empiricist– Experiments based on experiences, but experiments were blind.
- Methodists/ Routinists – Same methods can be applied on humans as used in plants, animals etc.
- The pharmacological industries took shape.
- Microbiology was born and increased knowledge of pathogenic microbes led to development of Antibiotics.
- Average life-span increased to 40-65 yrs.
- Discovery of anesthesia and antiseptics.
- Invention of Stethoscope (1816).
- Development of vaccines for Rabies and Smallpox.
- Invention of Sphygmomanometer (1881).
- Invention of Bifocal lens (1955).
- Discovery of X-rays.
Hahnemann was a man with passion for truth and spirit of scientific research, he believed that man should be studied as life force and body both equally.
SUMMARY
- Control of church authority faded away.
- Cruel treatment methods were freely used by physicians.
- Development in anatomy and physiology sciences.
- Physicians were divided in three major groups dogmatists, empiricists and Methodists.
- Hahnemann criticizes the treatment methods.
- Development of microbiology and vaccinations.
- Inventions of sphygmomanometer, stethoscope, and bifocal lens.
11.MODERN MEDICINE /20TH CENTURY

- Average life-span increased to 10 years.
- Development of PENICILLIN like antibiotics by Fleming, Florey & Chain.
- Discovery of INSULIN by Fredrick Bantin & Charles Best for successful treatment of diabetes.
- Development of Radio-Imaging Technology.
- Watson & Crick described the structure of DNA and explained how it carries the genetic information.
- Discovery of more vaccines.
- Development of PSYCHOLOGY.
- Ability to transplant organs and reattach broken body parts.
- Use of computers to aid in diagnosis, record keeping & research.
- Modified methods to care unborn fetus.
SUMMARY
- Penicillin and Insulin.
- More antibiotics.
- Structure of DNA.
- Radio imaging technology.
- Organ transplantation and reattachments.
- Use of computers.
12.21st CENTURY

- Completion of human genome project in 2003 which was started in 1990.
- Research of embryonic stem cells.
- Discovery of cloning process.
- Development of Bioterrorism.
- Outbreak of Pandemic diseases.
SUMMARY
- Human genome project.
- Embryonic stem cell research.
- Cloning, bioterrorism, pandemic diseases.
CONCLUSION
- Medical science is continually progressing.
- The sole duty of physician is to preserve the nobility of profession.
REFERENCE TERMINOLOGIES
Monasteries– Building occupied by communities of monks living under religious vows. In other word ashram, vihara, etc.
Bloodletting– Withdrawal of blood from patient in thought of reducing inflammation to prevent or cure the diseases.
Venesections/ Phlebotomy- Withdrawing of blood from circulatory system by incision.
Mustard plasters– A poultice (soft moist mass) of mustard seed powder spread inside a protective dressing and applied to the body surface in order to stimulate healing process.
Shotgun prescriptions- Careless, one sided single symptom prescriptions.
Leeches applications– Medical leeches are blood sucking parasites that live in freshwater. They were used in 19th century to heal wounds and restore blood circulation in veins.













Leave a Reply