Records of history shows that many different therapeutic methods of treatment were practiced in different parts all over the world, Dr. Hahnemann introduced some of the methods of treatment in Organon of medicine which are as follows,
- Antipathy/ Enantiopathy
- Allopathy
- Homoeopathy
- Isopathy
- Tautopathy
Table of Contents
ToggleANTIPATHY/ ENANTIOPATHY
Word-meaning
- The word antipathy is made up of two words namely, “Anti” means “Opposite” whereas “Pathos” means “Suffering”.
ANTIPATHY= ANTI (OPPOSITE) + PATHOS (SUFFERING)
Founding father
- A Greek physician Claudius Galenus/ Aelius Galenus (September 129 AD – 210 AD).
Principle
“CONTRARIA CONTRARIS CURANTER”
- English meaning- “Opposite Cures Opposite”.
Definition
- Treatment of diseases with the medicines that can produce exactly opposite symptoms of the disease symptoms.
Historical insights
- Hippocrates supported two systems of medicines
- Law of similar
- Law of dissimilar
According to him, cure is only possible by following the law of similar.
The second mode of treatment should be used only in incurable diseases.
- But Galen supported only the antipathic mode of treatment and the church authority in history made it compulsory.
- The dominance of this theory lasted for most of the 15th century till Paracelsus (1493- 1541) appeared.
- Hahnemann termed this system as Enantiopathy or palliative mode of treatment.
Because,
The opposite medicinal treatment cannot cure the disease
↓
When we prescribe the antipathic medicine, initially the disease seems like to be reduced in the intensity.
↓
But, the symptoms of the disease arise again with more intensity shortly after its relief.
↓
So, the condition of the patient becomes much worse than before.
Examples
- To a case of constipation, a remedy is prescribed that can produce diarrhoea.i.e. Opposite condition of the patient’s suffering.
- For case of burns, dipping of affected part in the cold water according to antipathic mode of treatment.
- A wine is prescribed to a weak and debilitated patient to make him active and energetic. Initially it acts as desired but shortly after patient may long for more quantity of wine to get the same stimulation.
Conclusion
- Initial effects of antipathic mode of treatment produces desired results.
- But more amount of those may produce medicinal diseases or addiction.
- Patient’s condition may get worse than before.
Advantages
- In case of emergency patients, palliative medicines relieve the patient’s suffering.
- When there is difficulty in diagnosis of symptoms such as in unconscious patients, this method can be useful.
- In case of incurable diseases, this method helps to relieve at least the suffering of the patient.
Disadvantages
- All the symptoms cannot be removed, so cure is not possible.
- As it is the palliative treatment, the recurring symptoms appears with more intensity which makes the case more difficult to cure.
- Every time need for increase in dose may produce iatrogenic disease.
- Not all the symptoms can be treated antipathicaliy, so this method cannot be applied universally.
ALLOPATHY/ HETEROPATHY
Word meaning
- The word allopathy is a Greek derivative of two words “ALLOS” which means “Dissimilar” or “Heterogeneous”, where as “Pathos” means “suffering”.
- This word was coined by Dr. Samuel Hahnemann in 1810.
ALLOPATHY= ALLOS (DISSIMILAR) + PATHOS (SUFFERING)
Principle
- No fixed principle.
Founder
- Allopathy has no therapeutic law of its own with no founder.
- It applies many principles of other sciences according to the requirements of the given case. So, it cannot be called the ideal method of cure.
- In 19th century it was referred as HEROIC MEDICINE in Europe and North America.
- Dr. Hahnemann intended to explain “How the physicians with conventional therapeutic methods merely treated symptoms and failed to cure the underlying disease”.
Definition
- A medical therapy with no relation between symptoms of drug and disease.
- There is no direct relation between the pathogenesis of medicine and disease.
- Use of any approach which they think best suitable to the given case.
Methods of treatment
- Use of large and crude doses of medicine.
- Use of compound mixture of medicines.
- Diagnosis of disease on the bases of material substance as the causative factor of disease.
- Prescription of a specific medicine based on diagnosis.
- Medicines are proved on lower animals.
- More importance is given to the Material and pathological aspects of organism.
- Employment of large crude doses for long period.
Disadvantages
- Long term use of large doses may cause harm to the patient.
- No individualizing approach towards the patient.
- Only treatment of parts, organs and symptoms may possible. But no possibility for holistic approach.
- Chronic diseases remain untreated.
- May cause the development of medicinal diseases.
- Use of synthetic drugs and surgical procedures to treat the diseases.
Advantages
- In case of acute emergencies allopathy can provide a great deal of relief to the suffering of patients.
- Antibiotic medicines used in allopathy have served countless human lives.
- More rapidly accepted by health insurance.
HOMOEOPATHY
Word meaning
The word Homoeopathy is made up of two Greek words.
- “Homoeos” = Similar
- “Pathos” = Suffering
HOMOEOPATHY = HOMOEOS (SIMILAR) + PATHOS (SUFFERING)
Founding father
- Dr. Samuel Hahnemann, a German physician (1755-1843).
Principle
“SIMILIA SIMILIBUS CURENTUR”
- English meaning- “Like cures like”/ “Let likes be cured by likes”.
Definition
- Homoeopathy is a therapeutic system of medicine which treats the diseases by administering the medicines that can produce exact similar symptoms in a healthy individual.
Explanation
- Homoeopathy is based on the law of similar.
- The recognition of this is of very ancient in origin.
- Hippocrates identified the law of similar as the only curative law in the universe.
- Hahnemann made this law therapeutically applicable and made it harmless.
- Hahnemann used to say “Treat the patient and not the disease”.
- Each patient is approached individually as a whole.
- Homoeopathic medicines are very well proved and verified on healthy human beings of both sexes.
- Homoeopathic medicinal substances are potentised (but not in crude form), this is why they are harmless.
- It is the only curative method of treatment.
Advantages
- Individualistic approach in treating the patient.
- No possibilities for harmful effects of drugs.
- Its holistic approach covers both physical and mental symptoms of the patient.
- Causes of the disease are focused in order to cure.
- Application of single, simple and minimum medicinal drug substance at a time.
- Homoeopathy is very good when it comes to treat the chronic diseases.
- Homoeopathic medicines do not palliate or suppress the symptoms.
Limitations
- Homoeopathy has less scope in acute emergency cases.
- Limited scopes where there is advancement of pathology.
- Do not work as a supplement therapy.
- They have limited scope in the field of vaccination.
You can read the scopes and limitations of homoeopathy in detail by following the link here, SCOPE AND LIMITATIONS OF HOMOEOPATHY.
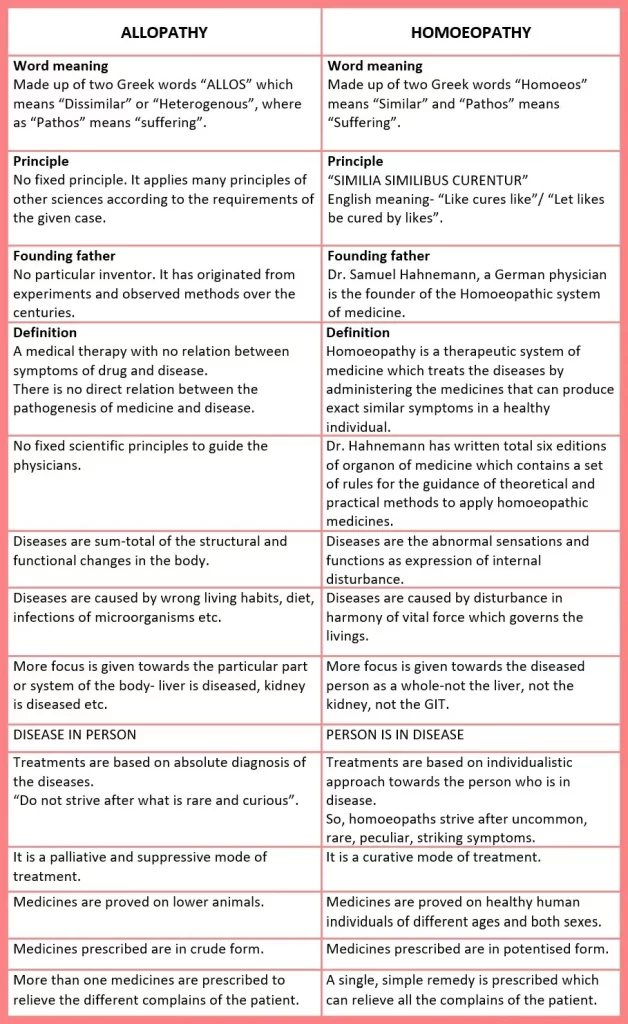
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN ALLOPATHY AND HOMOEOPATHY
ISOPATHY
Word meaning
- The word Isopathy is made up of two words “ISO” which means “SAME”
- Whereas “PATHOS” means “SUFFERING”.
ISOPATHY= ISO (SAME) + PATHOS (SUFFERING)
Principle
“EQUALIA EQUALIBUS CURENTUR”
- English meaning- “Same cures same”.
Founding father
- Dr. Willum Lux of Leipzig who was a homoeopathic veterinary surgeon.
- Books written by him on Isopathy- “The Isopathy of contagions”.
Definition
- It is the therapeutic system of medicine which treats the diseases by same contagious substance that produces the disease.
Examples
- To a patient suffering from burns, hot packs will be applied on the burnt parts.
- To a case of frost bite, snow will be applied to the affected area.
- To a patient of Otorrhoea, administration of the dilution of his own ear discharge.
- Isopathy is not homoeopathy. But it clearly is a misconception of the law of similar.
- There is a difference between the same and the similar.
The same- identical/equal from one another.
The similar- it means to have resemblance in appearance/ character or quantity without being identical.
- Practicing Isopathic methods of treatment almost disappeared itself during the time of Dr. Hahnemann because,
- Only selective cases could be cured.
- Cures in Isopathy might happened only in accidental ways.
- No reliability.
- No sufficient records of proving available.
- Isopathy may cause harm and lead to dangerous condition.
Reference
Homoeopathic Nosodes like Influenzinum, Psorinum, Tuberculinum, Mezerium etc. may look like Isopathy but it is not true because,
- Every Nosodes in Homoeopathy are proved on healthy human beings.
- They are reverified before clinical applications.
- They are being potentised before proving.
- They are prescribed on the basis of symptom similarity.
- They are selected on the bases of the totality of the symptoms (not the material causes of the disease).
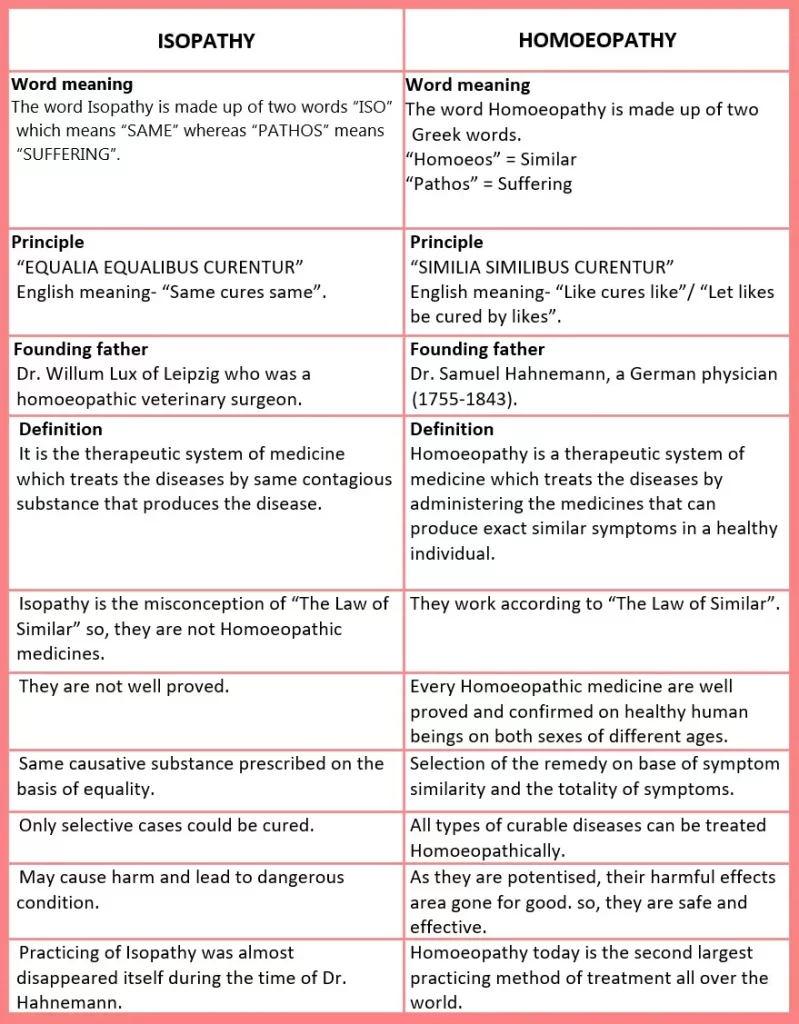
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN ISOPATHY AND HOMOEOPATHY
TAUTOPATHY
Word meaning
- The word Tautopathy is made up of two Greek words “TAUTO” means “THE SAME”, whereas “PATHOS” means “SUFFERING”.
TAUTOPATHY= TAUTO (THE SAME) + PATHOS (SUFFERING)
Principle
- It is based on “Arndt-Schultz law”.
Founding father
- Dudley Wooton Everitt a famous pharmacist of England and the former director of Nelsons Homoeopathic pharmacy.
Arndt-Schultz law- Introduced by,
- Rudolph Arndt (1835-1900) a German psychiatrist and homoeopath.
- Hugo Paul Friedrich Schultz (1853-1932) a German pharmacologist and toxicologist.
- They together invented a physiological law,
“For every substance Small dose stimulate, Medium doses inhibit, Large doses kill”.
- According to this law, a drug substance will have opposite effect in its small dose than in its large dose, which is known as “Biphasic response of the drug”.
- This law describes the action of the drug substance in different doses.
Definition
- treatment of drug induced diseases with the help of the same causative drug substance but in potentised form to antidote the bad effects of the crude drug substance.
Examples
- The bad effects of chloroform are removed by the potentised chloroform.
- The bad effects of sulpha drugs are removed by the potentised sulpha drugs.
Arndt-Schultz law can be found in the old books of allopathic pharmacology.
It supports the potentization of the drug substances and curative effects of minimum doses.
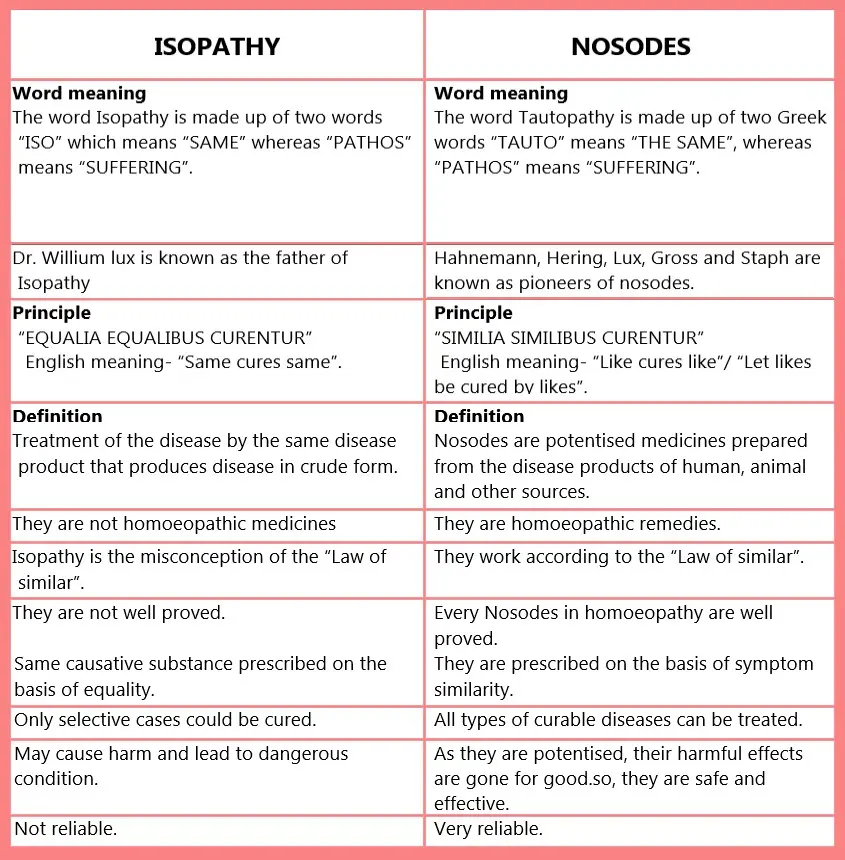
DIFFEENCE BETWEEN ISOPATHY AND NOSODES
Now you have the sufficient knowledge about Different modes of treatment introduced by Dr. Hahnemann.

want PDF of this topic to download.
The content of this site is copyrighted and original so it can not be downloaded or copied…but you are always welcome to read and solve your queries from the site here.
Thanks & regards.