Cellular organelles are special and permanent components that remain inside the cell.
They have characteristic shapes which are bounded by limiting membrane.
They contain their own set of enzymes and perform certain biochemical functions like growth, maintenance and reproduction.
These organelles help in maintaining the homoeostasis.
They are broadly classified into two:
- Non-membrane bound cell organelles
- Membrane bound cell organell

Here, in this post we will be discussing the non-membrane bound organelles of the cell.
NON-MEMBRANE BOUND CELLULAR ORGANELLES
- Ribosomes/polysomes
- Centrosomes
- Cilia and flagella
Table of Contents
ToggleRIBOSOMES
They are the tiny spherical structures of the cell.
They are made up of 35% of protein and 65% of Ribonucleic acid (RNA).
Due to its high content of RNA, they are called as Ribosomes.
RNA present in ribosomes is known as Ribosomal RNA or rRNA.
Structure of Ribosomes
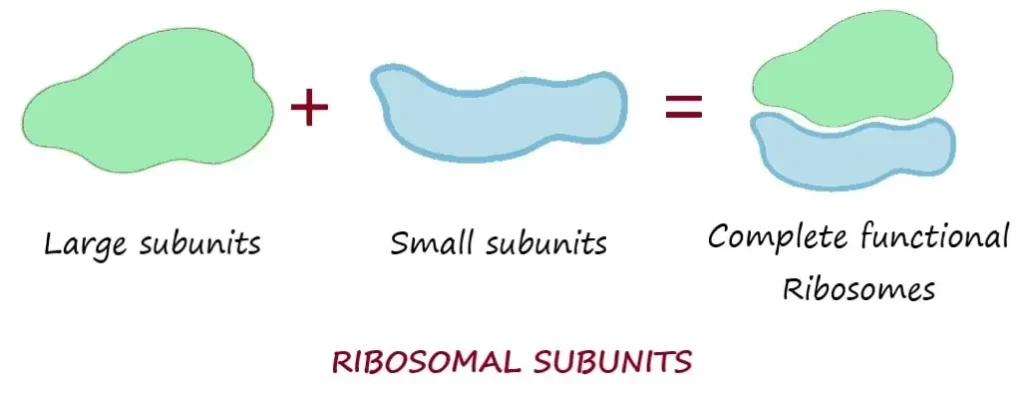
Made up of two subunits.
Large subunits and small subunits both are separately made in nucleus.
Once made, they exit separately from nucleus then come together in the cytoplasm.
Types of Ribosomes
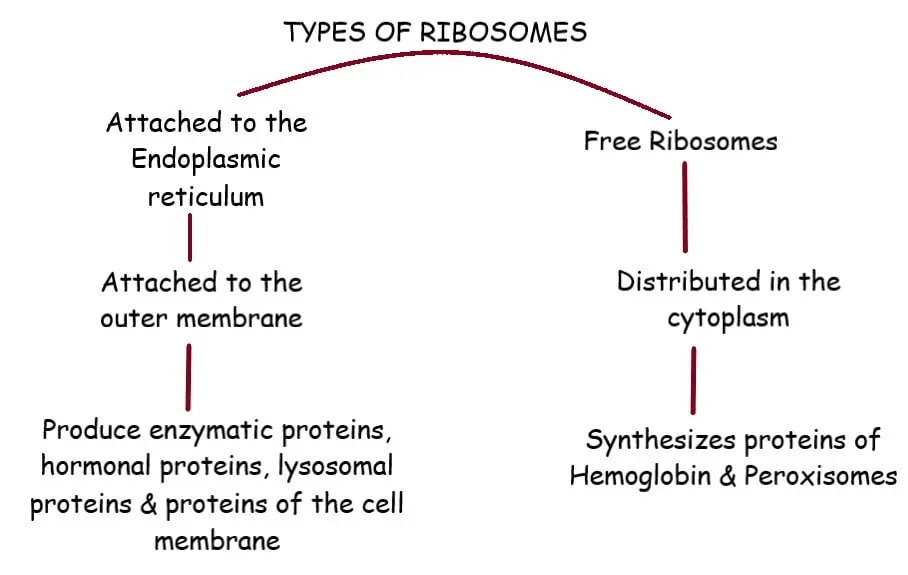
Made up of two subunits.
Large subunits and small subunits both are separately made in nucleus.
Once made, they exit separately from nucleus then come together in the cytoplasm.
Types of Ribosomes
CENTROSOMES
Centrosomes are located close to the nucleus.
Contains two components
Pair of centrioles
Pericentriolar material
1. Pair of centrioles/two centrioles
- Cylindrical structures
- Each one made up of 9 clusters of 3 microtubules (triplets).
- They are arranged in circular pattern.
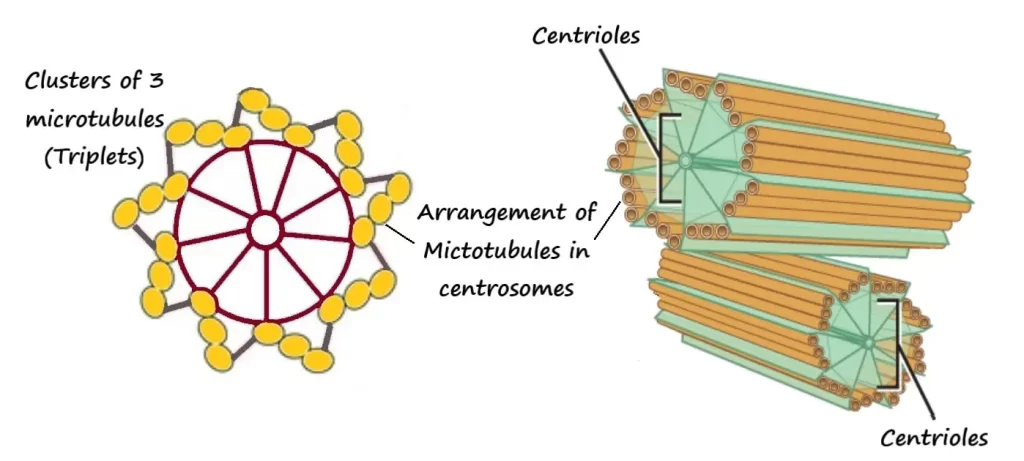
- These both centrioles are arranged in such a way that long axis of one lies at a right angle to the long axis of other centriole.
2. Pericentriolar material
- Surrounds centrioles.
- Contains hundreds of ring-shaped complexes which are made up of tubulin protein.
- These proteins play very important role in cell division and microtubule formation.
Functions of Centrosomes
Centrioles facilitates the movement of chromosomes during cell division.
Centrosome replicates during cell division so that subsequent generations of cells also can have capacity of cell division.
Think of a cell that do not have a centrosome, what can you think about its ability of cell division?
CILIA AND FLAGELLA
These are projections of the surface of cell which are motile.
CILIA
Cilia means eyelashes.
Single cilia are called cilium.
They are short, numerous, hair like projections arising from the cell surface.
Each cilium is fixed to a basal body lying underneath the surface of plasma/cell membrane.
CILIARY MOVEMENT
- Well-coordinated.
- Oar like pattern of beating.
- Stiff during power stroke (imagine an oar driving into the water).
- Flexible during recovery stroke (oar moving above the water).
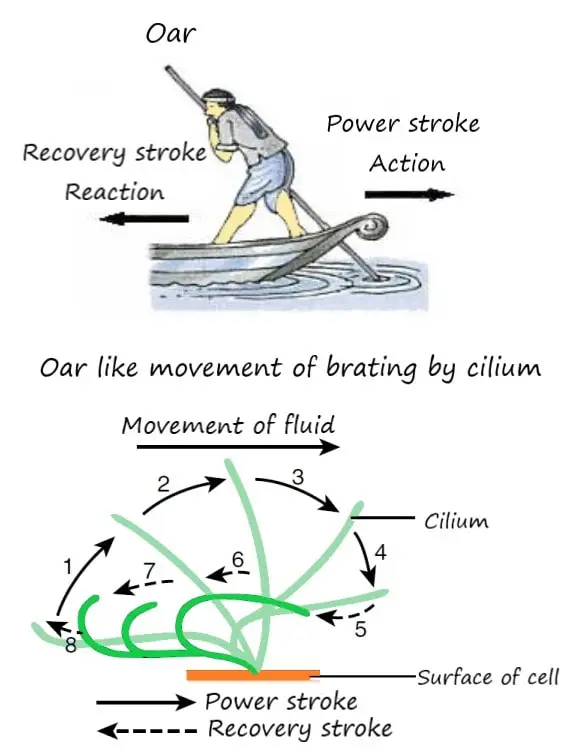
- Cilia causes constant movement of fluid through the cellular surface.
Example: thousands of cilia on the respiratory surface wipes away the trapped foreign particles in mucus.
Applied physiology
Nicotine in Cigarette vapor paralyzes the movement of cilia.
This is the reason of frequent coughing in smokers to remove foreign particles from their air-duct.
Cilia present in fallopian tubes sweeps oocytes towards the uterus so, females with smoking habits may have increased risk of ectopic pregnancy.
FLAGELLA
Flagella is a thin, thread like structure which is originates from certain cell bodies.
Flagella are similar to the structure of cilia but much longer than them.
Single flagella are called flagellum.
They usually move whole of the cell.
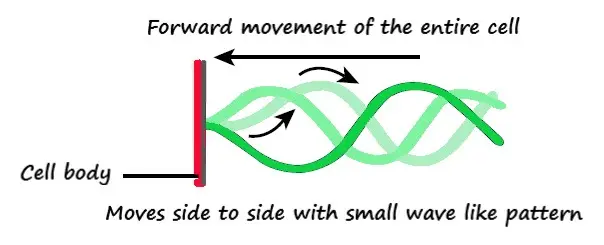
Sperm cell tail is the only example of cell with flagellum in human body.
Flagellum in sperm cell propels the cell body toward the oocyte in fallopian tubes.
MEMBRANE BOUND CELLULAR ORGANELLES
Membrane bound organelles are described in a separate post which you can read by following the links given below.
Single membrane bound organelles
- Golgi apparatus/Golgi complex
- Rough endoplasmic reticulum/RER
- Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
- Lysosome
- Peroxisomes
- Proteosomes
Double membrane bound organelles













Leave a Reply