ASO (Antistreptolysin O) Titre Blood Test is advised by a physician to determine whether a previous streptococcal infection (Tonsillitis, Throat infection, Skin infection etc.) has caused any complications.
Table of Contents
ToggleFull Form of ASO
- Anti-Streptolysin O
Word Meaning
ANTI- Means Against to.
STREPTO- Related to Streptococcus Pyogenes
LYSIN- An antibody which is capable of breaking down the cell wall (especially bacterial cells).
O- Stands for Oxygen labile.
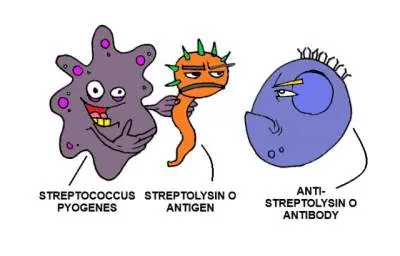
Streptolysin O
Streptolysin is a type of Haemolytic toxin which is made up of protein that is produced by some strains of streptococci bacteria.
Streptococci are Gram-positive bacteria which are found in chains, they are non-motile and facultative anaerobes. (For detailed information, follow the link, Streptococcus Pyogenes).
They produce some harmful toxins like Streptolysin S and Streptolysin O along with some enzymes like DNases, Streptokinase etc.
In 1930, Dr. E. W. Todd discovered Two toxins that are responsible for the breakdown of cell walls of RBCs (Erythrocytes).
They are, Streptolysin S and Streptolysin O.
Streptolysin S is stable in presence of Oxygen in the atmosphere, whereas Streptolysin O is oxygen labile (Liable to change or alter easily in the presence of oxygen).
Antistreptolysin O (ASO/ASLO)
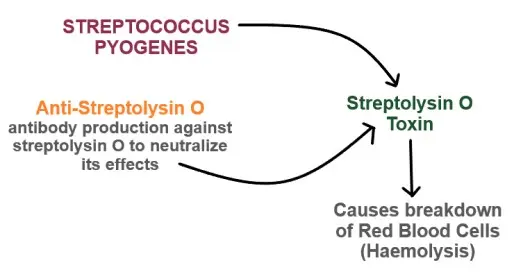
- When your body comes in the contact with harmful bacteria, it produces the substances made up of protein known as antibodies to defend itself against these pathogenic bacteria.
- ASO is also an Antibody.
- Specially produced against the streptococcal infection in the body.
- It combines and neutralizes the haemolytic effects (breakdown of Red blood cell walls) of Streptolysin O toxin which is produced by Streptococci bacteria.
- This antibody can be found in serum of the patient from 1 week to 1 month after the onset of infection.
- The amount of ASO Titre (antibody) reaches to its maximum at about 3 to 5 weeks after the infection.
- ASO and Anti-DNases are the most commonly found antibodies which are produced as body’s immune response against Group A streptococcal infection.
Usually, a patient having streptococcal sore throat recovers within a few days or may receive antibiotic treatment to kill the bacteria.
But some patients don’t develop any symptoms of infection while some may not even know that they need treatment.
These untreated infections can lead to future complications.
These complications are known as post-streptococcal complications.
Examples: Scarlet fever, Rheumatic fever, Acute Glomerulonephritis etc.
Anti-Streptolysin O Blood Test
- It is a Serological test (Scientific study of the serum and other body fluids of suspected patients).
- Helps to Identify the history of streptococcal infection.
- This test is used to confirm the diagnosis of Rheumatic fever and Glomerulonephritis in the presence of symptoms.
- This test is advised especially when it is not possible to isolate streptococcal group in laboratory culture.
- The presence of High level of ASO antibodies in the serum of patient indicates the extent and degree of post-streptococcal infection.
- Elevated ASO level also may be present in some other conditions like Scarlet fever, Acute rheumatoid arthritis, Tonsillitis and various other post-streptococcal infections.
When To Test For ASO?
This test is advised when a physician suspects the cause of disease may be due to any previous infection.
In other words, when a patient shows the symptoms of fatigue, chest pain, shortness of breath, rheumatic fever, oedema (fluid accumulation), darkness of urine with symptoms of glomerulonephritis after the recent history of infection with Group A streptococci (GAS) bacteria.
Especially those who were not properly diagnosed and treated.
Requirement Of The Test
- A vial of blood drawn from vein of the patient.
- Patient should not eat at least 6 -8 hours prior to the sample collection.
- If the patient is having steroids or antibiotics, he should be asked to discontinue to achieve accurate results.
Principle Of ASO Test
The amount of ASO antibody in blood depends on the production of streptolysin O by streptococci in the infected patient (host).
Commercially available testes are
- Anti-streptolysin O Latex test- Performed to detect a significant raise in ASO titre.
- Anti-streptolysin O titration test- Used to determine the titre of ASO antibody.
Titre or Titer
- Titre word is a Latin derivative of a word “Titulus”.
- Americans spell it “Titer” whereas English spell its “Titre”.
- Titre is the degree of dilution of a substance such as Antibody.
- A titration test is a blood test done in laboratory to check the presence of certain antibodies in the blood.
- If the high concentration of specific antibody in the serum sample is detected, the titre is read as higher.
- A low concentration or undetectable titre indicates a small number of antibodies in the serum.
Normal ASO Titre range
Children- < 150 IU/ML
Adults- <200 IU/ML
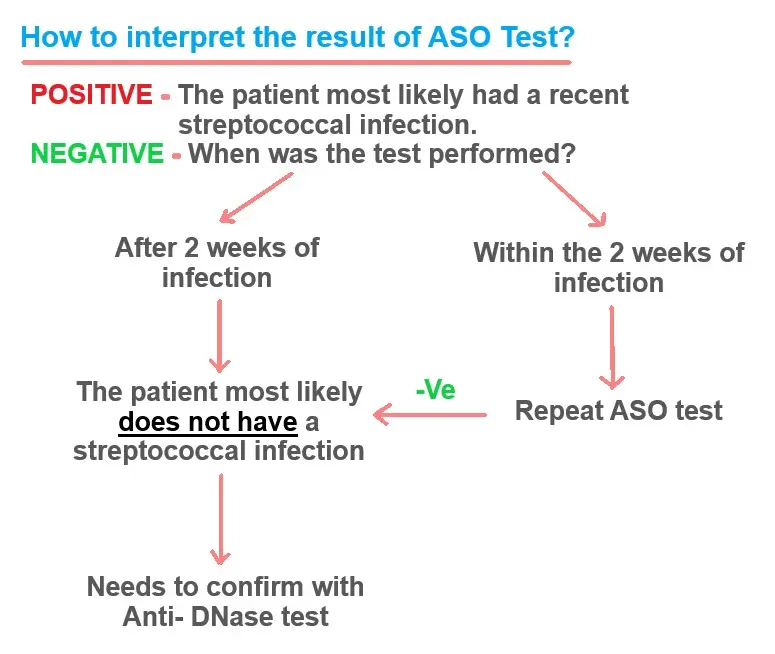
How to Interpret the Results?
- A NEGATIVE ASO or Very Low Titres: This means that the patient tested most likely did not had any recent streptococcal infection (Specially if the sample collected on 10 to 14 days after the onset of infection).
- Combining with an Anti-DNase B test is also found negative.
- A POSITIVE ASO: An elevated level of ASO titre suggests that the patient has had a recent history of streptococcal infection.
- Signs of resolving infection are: Initially positive ASO Titres start to decline suggests that an infection might occur and may be resolving now.
Limitations Of The ASO Test
- If the patient is having Steroids which suppress the immune system, can also suppress ASO production and ASO result may occur as false negative.
- Skin infection by Group A streptococcus bacteria may not produce an ASO antigen.
- Increased level of Beta lipoproteins (fats) in blood also can neutralize Streptolysin O toxin and ASO titre can show false positive result due to remaining (non-utilized) ASO antibodies in blood.
- Use of antibiotics also may reduce the number of bacteria and suppress the production of ASO antibodies.
- Can not predict whether the complications that will occur following a streptococcal condition.
- Can not predict the severity of the disease.
- Some non-streptococcal conditions also may show the rise of ASO titre such as Tuberculosis, Hepatitis, Gonorrhoea etc.
Conclusion
ASO test detects only past infection.
Positive results help in diagnosis of Rheumatic fever and Glomerulonephritis.
Most reliable method to identify the current/acute infection.
- Throat culture
- Rapid strep test
